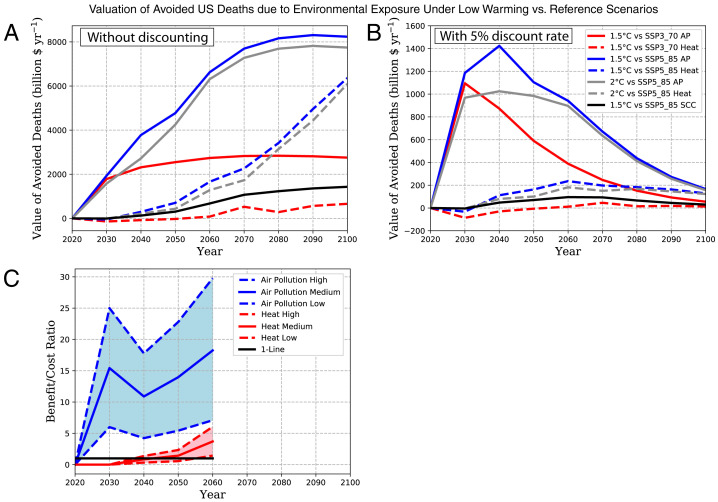
Fig. 7.
Valuation of avoided US premature deaths attributable to air pollution and heat exposure under the 1.5 °C (SSP1_19) and 2 °C (SSP1_26) scenarios relative to the lower (SSP3_70) and higher (SSP5_85) reference cases evaluated both without discounting future impacts (A) and with a 5% discount rate (B). Benefit/cost ratios for 2 °C (SSP1_26) relative to the higher (SSP5_85) reference case over the next several decades using costs from Williams et al. (23) as “High,” Markanya et al. (22) as “Low,” and McCollum et al. (24) as “Medium” (C). Lines labeled “AP” are impacts due to air pollution and valuation using a standard social cost of carbon approach is labeled SCC. The valuation analysis extends to 2100 to include long-term impacts of heat (SI Appendix).