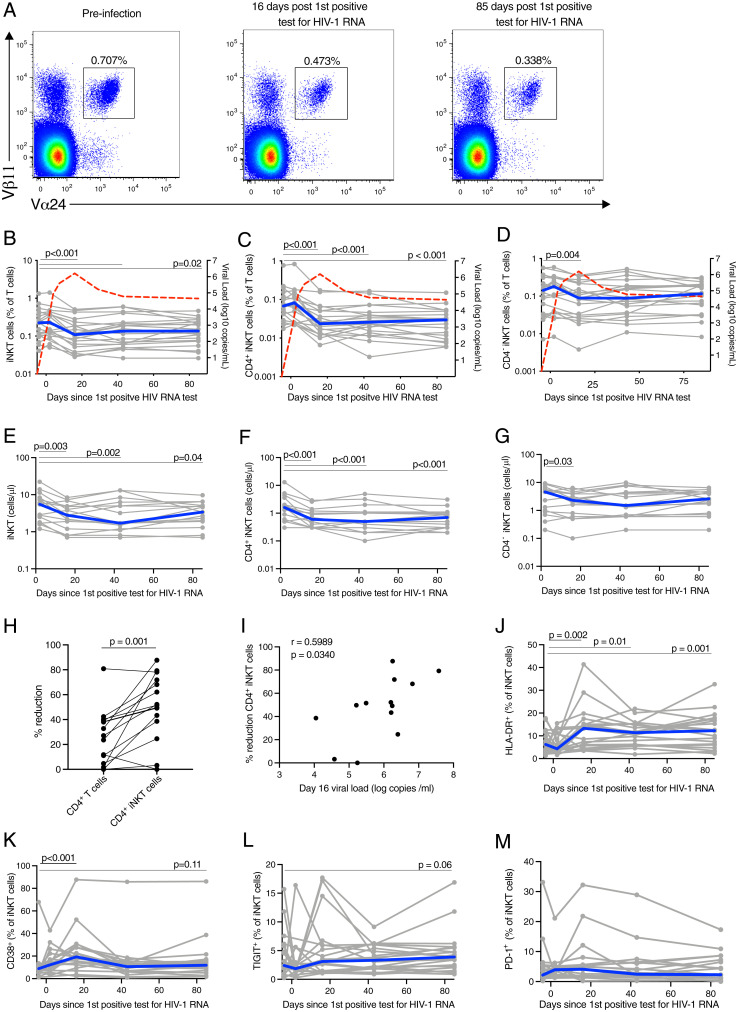
Fig. 1.
Peripheral blood CD4+ iNKT are reduced early in untreated AHI. (A) Representative flow plots showing the frequency of peripheral blood iNKT in acute, untreated HIV-1 infection. Frequency of peripheral blood iNKT (B), CD4+ iNKT (C), and CD4− iNKT (D) cells in acute, untreated HIV-1 infection. Individual subjects are shown in gray and the median in blue. The red line represents the median VL. Absolute cell count of peripheral blood iNKT (E), CD4+ iNKT (F), and CD4− iNKT (G) cells in acute, untreated HIV-1 infection. (H) Percentage of absolute cell count reduction for conventional CD4+ T cells and CD4+ iNKT cells. (I) Association between the VL at day 16 after the first HIV RNA–positive test and the percentage of CD4+ iNKT cell reduction. Expression of HLA-DR (J), CD38 (K), TIGIT (L), and PD-1 (M) by peripheral blood iNKT cells in acute, untreated HIV-1 infection. Time points sampled are indicated by the circles. n = 20 for all plots, except for E, F, G, and H in which n = 15 and I in which n =13.