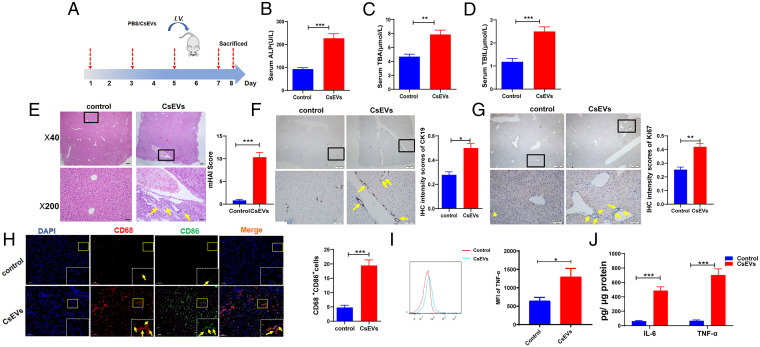
Fig. 3.
CsEVs cause severe biliary injuries. (A) The study design. The mice that were intravenously injected with CsEVs (0.5 mg/mL, ∼100 μL) or PBS (100 μL) at the indicated time. (B–D) The levels of serum indicators for biliary injuries, such as ALP (B), TBA (C), and TBIL (D) in the mice treated by CsEVs or PBS. (E) H&E staining showing histological changes (Left) was evaluated using mHAI scoring (Right) in the liver of mice treated with CsEVs or PBS; yellow arrows showed infiltered immune cells. (F) The expression of CK19 (yellow arrows) in the liver of mice treated with CsEVs or PBS by IHC staining. (G) The expression of Ki67 (yellow arrows) in the liver of mice treated with CsEVs or PBS by IHC staining. (H) The proportion of CD86+CD68+macrophages (M1-like, yellow arrows) in the livers of mice that were hydrodynamically injected with CsEVs or PBS as determined by immunofluorescence assay. (I) TNF-α–producing macrophages (CD11b+F4/80+) in livers of these mice were detected using flow cytometry. (J) The levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in the livers of mice were determined by ELISA. The values were expressed as mean ± SEM. Compared with indicated groups, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.