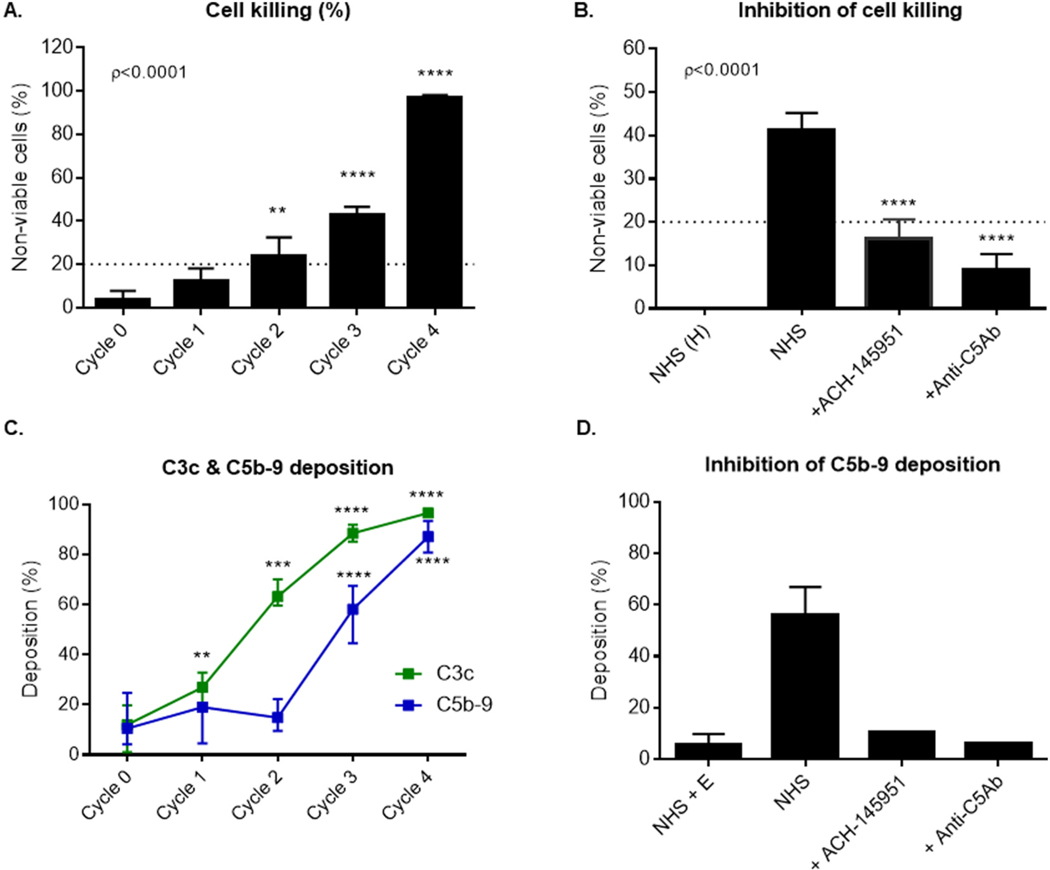
Fig. 1.
C3b accumulation on the cell surface leads to increased cell killing and C5b-9 deposition, which is blocked by complement inhibitors. (A) TF1 PIGAnull cells loaded with one to four cycles of C3b were incubated in 20% human serum and cell killing was measured using the mHam. (B) Cells loaded with 3 cycles of C3b were incubated with NHS alone, NHS and ACH-145951 (0.3 μM), or NHS and anti-C5 antibody (50 μg/ml). Cell killing was measured using the mHam. (C) Cells loaded with one to four cycles of C3b were incubated in 20% human serum. C3c and C5b-9 deposition was measure by flow cytometry. (D) Cells loaded with 3 cycles of C3b were incubated with NHS, NHS and ACH-145951 (0.3 μM), or NHS and anti-C5Ab (50 μg/ml). Data shown as mean ± SEM of triplicate wells and representative of three independent experiments. Normal Human Serum (NHS), Heat Inactivated Normal Human Serum (NHS(H)), factor D inhibitor (ACH-145951), anti-C5 antibody (anti-C5Ab), Normal Human Serum and EDTA (NHS + E), ** p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001.