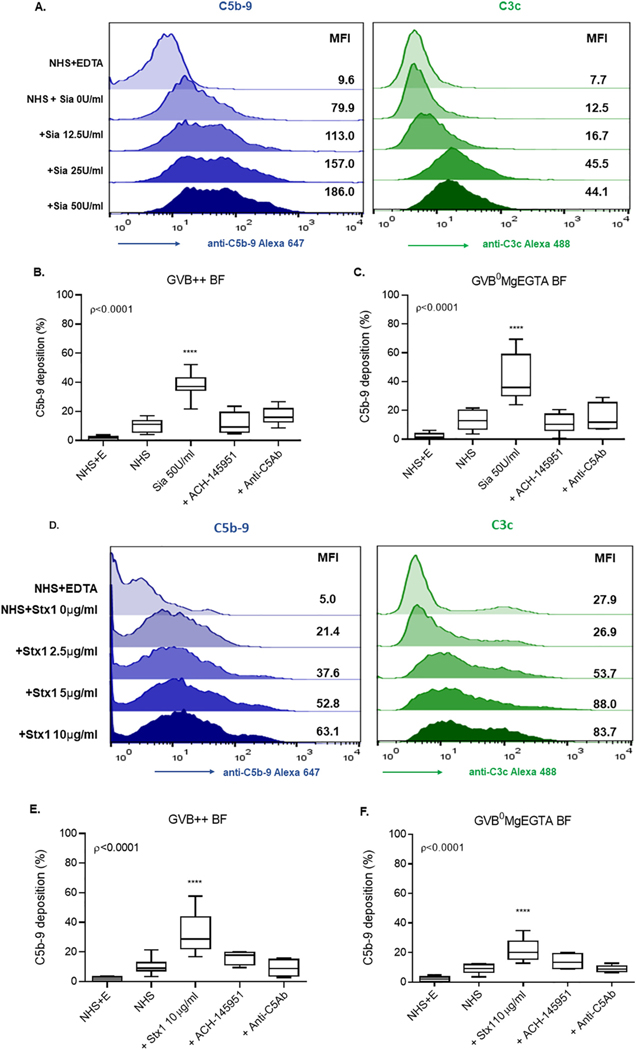
Fig. 3.
Sia and Stx1 induce C5b-9 and C3c deposition on the cell surface. (A) Histogram overlays showing C5b-9 (blue) and C3c (green) deposition following Sia treatment of cells in GVB++ buffer. C5b-9 deposition on Sia treated cells in the presence of ACH-145951 (1.0 μM) and anti-C5Ab (50 μg/ml) in (B) GVB++ or (C) GVB°MgEGTA. (D) Histogram overlays showing C5b-9 (blue) and C3c (green) deposition following addition of Stx1 in GVB++. C5b-9 deposition in the presence of ACH-145951 (1.0 μM) and anti-C5Ab (50 μg/ml) in (F)GVB++ and (E) GVB° MgEGTA. Data shown as mean ± SEM of triplicate wells and are representative of three independent experiments. Normal Human Serum (NHS), Sialidase (Sia), Normal Human Serum and EDTA (NHS+E), Factor D Inhibitor (ACH-145951), Anti-C5 Antibody (anti-C5Ab), Shiga toxin 1 (Stx1), ****p < 0.0001.