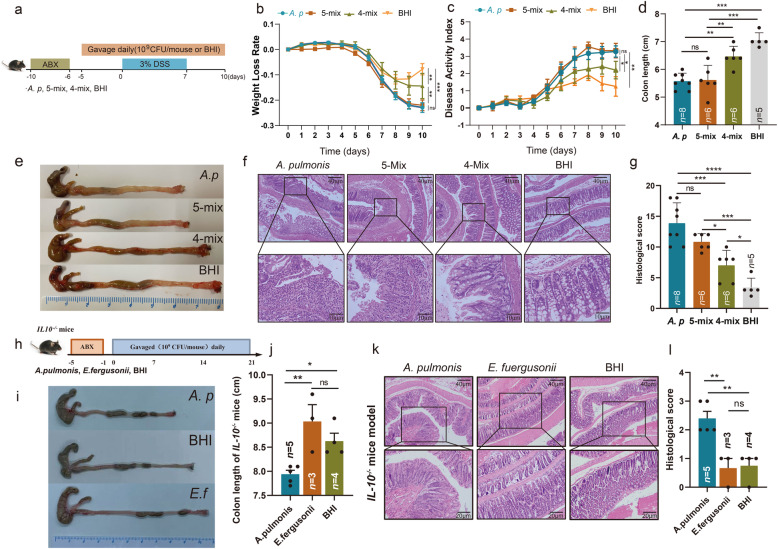
Fig. 4.
A. pulmonis is sufficient to elicit a strong inflammatory response in mice. a SPF C57BL/6 mice were treated with an antibiotic cocktail for 4 days. One day post antibiotics, the mice were daily orally colonized with bacterial cocktail (A. pulmonis, 5-Mix or residual 4-Mix, 109 CFU/mouse/dose) or BHI until being euthanized. After 5 days bacterial colonization, the mice were exposed to 3% DSS for 7 days, followed by regular water for 3 days. b and c Changes of body weight (b) and disease activity index (DAI) (c) after 3% DSS administration. d–g Colon length (d), representative colons (e), representative colonic histological images (Scale bar = 40 μm and 10 μm) (f), colonic histological score (g) in mice treated with A. pulmonis, 5-mix bacterial cocktail, 4-mix bacterial cocktail and BHI. h SPF Il10−/− mice were treated with antibiotics cocktail for 4 days. One day post antibiotics, the mice were daily orally colonized with bacterial cocktail (A. pulmonis or E. fergusonii, 109 CFU/mouse/dose) or BHI for 3 weeks. i-l Colon length (i), representative colons (j), representative colonic histological images (Scale bar = 40 μm and 20 μm) (k), colonic histological score (l) from Il10−/− mice treated with A. pulmonis, E. fergusonii and BHI. Results are shown as the mean± SEM. Each dot indicates an individual mouse. The statistical significance values are denoted as: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. One-way ANOVA following Tukey’s multiple comparison test (d, g, j, and l); two-way ANOVA following Tukey’s multiple comparison test (b and c)