Figure 4.
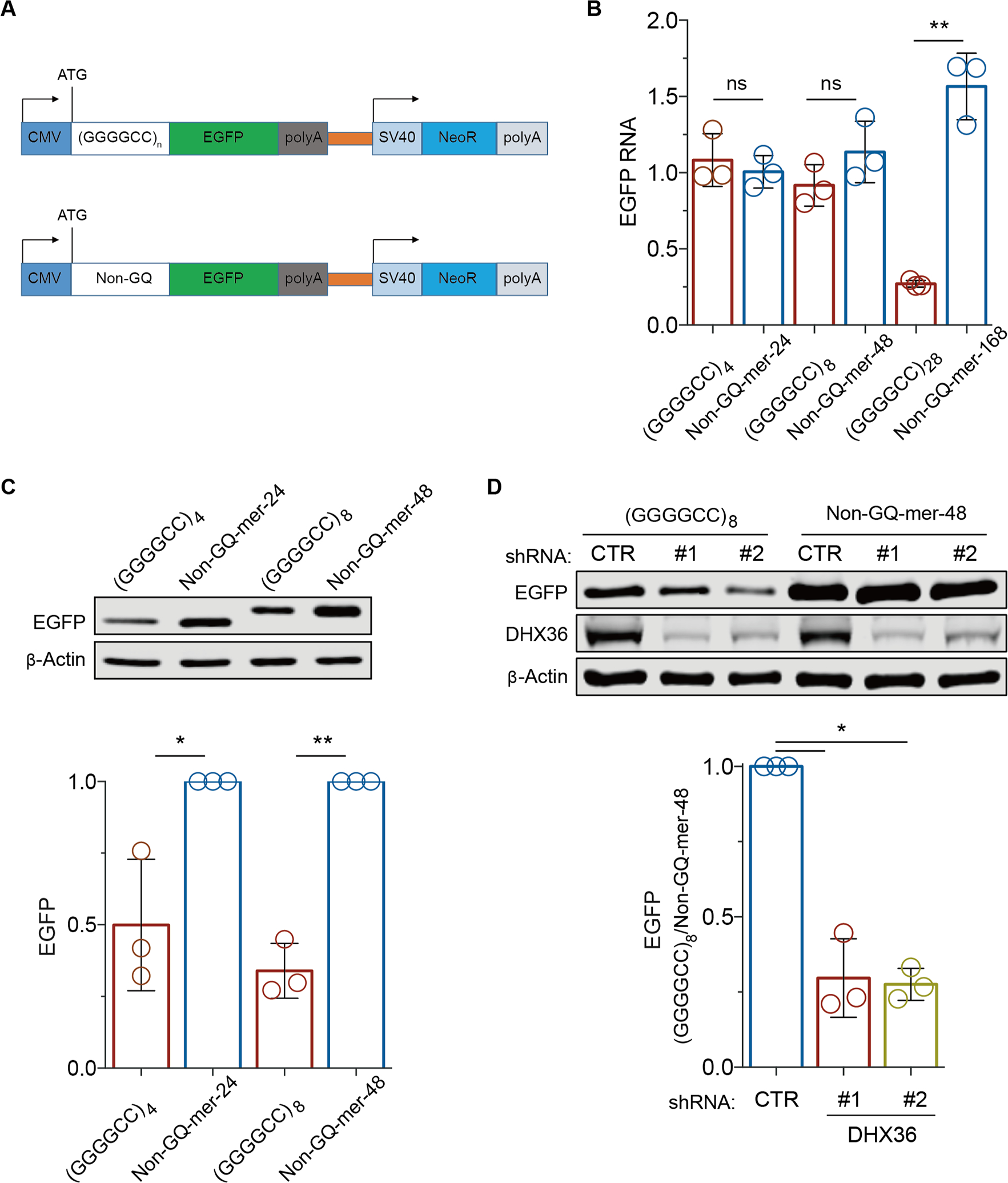
DHX36 is required for efficient translation elongation through GGGGCC repeat RNAs. (A) Schematic of the reporter constructs used to monitor the effects of (GGGGCC)n repeats on translation elongation. (B) The effects of (GGGGCC)n repeats on transcription were compared by RT-PCR analyses of EGFP RNA levels in HEK293 cells expressing reporter constructs containing various GGGGCC repeats and non-G-quadruplex-forming control sequences (non-GQ-mers) of the same sizes. The level of EGFP RNA was normalized to that of NeoR RNA, which is independently expressed on the same reporter construct. (C) Immunoblot analysis of EGFP from HEK293 cells expressing the reporter and control constructs. β-actin was used as the loading control. (D) Immunoblot analysis of EGFP from HEK293 cells expressing the reporter and control constructs after the cells were treated with shRNAs against DHX36 or non-targeting control shRNAs. Data are given as means ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
