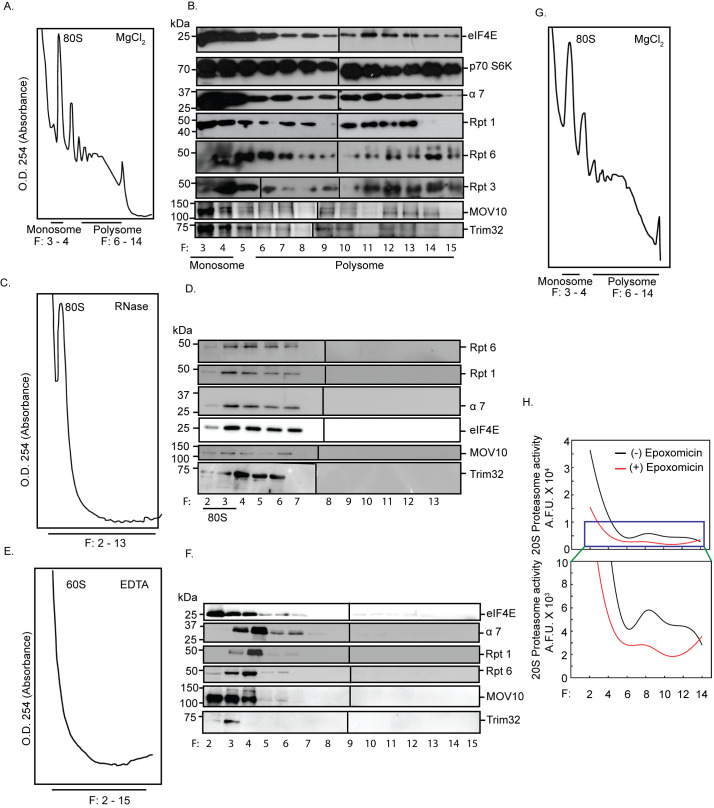
Fig 3. RNA-dependent association between active proteasomes and translating polyribosomes.
Absorbance profile at 254 nm (A254) and western blot analysis of fractionated cytoplasmic extracts from hippocampal tissue incubated in the absence or presence of MgCl2 or RNase or EDTA. Monosome (80S), 60S ribosome, and polysome fractions are as indicated. Western blots performed from tri-chloroacetic acid–precipitated fractions to determine the distribution of the translation regulators eIF4E and p70 S6K; α7 subunit of the 20S core of the proteasome, Rpt1, Rpt3, Rpt6 of the 19S cap, and miRISC proteins MOV10 and Trim32 in the presence or absence of MgCl2 or RNase or EDTA. (A) A254 profile in the presence of MgCl2. (B) Western blots of the fractions obtained in (A). (C) A254 profile obtained in the presence of RNase. (D) Western blots of the fractions obtained in (C). (E) A254 profile in the presence of EDTA. (F) Western blots of the fractions obtained in (E). Rpt3 blots with different exposures are distinguished by a vertical black line to denote they represent separate panels within the figure. Two blots with different exposures are shown in the main figure and raw data to visualize the specific band of Rpt3. (G) A254 profile of fractionated cytoplasmic extract used for determining activity of proteasomes. (H) Quantitation of catalytic activity of proteasomes present in alternate fractions from two polysome preparations. See also S2 Fig. The data underlying this figure are available at https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/Homeostatic_scaling_is_driven_by_a_translation-dependent_degradation_axis_that_recruits_miRISC_remodeling/16768816. miRISC, miRNA-induced silencing complex; p70 S6K, p70 S6 kinase.