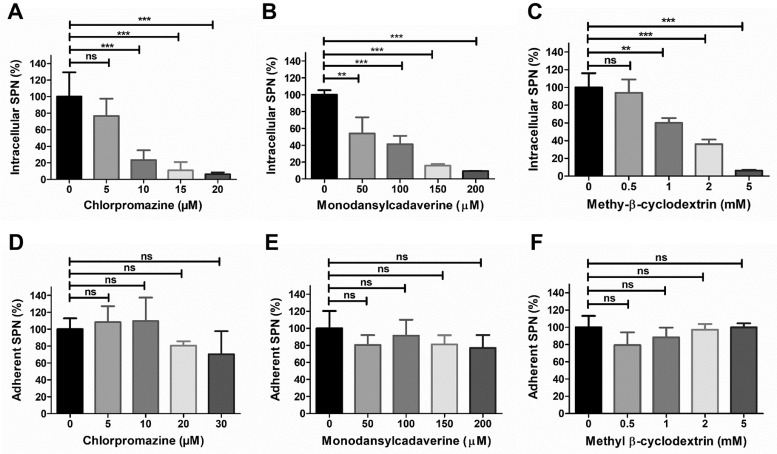
Fig. 1.
S. pneumoniae invades brain endothelium using clathrin and caveolae dependent endocytic pathways. Intracellular (A-C) or adherent (D-F) SPN to hBMEC were determined following treatment with different concentrations of clathrin pathway inhibitors Chlorpromazine (A, D) and Monodansylcadaverine (B, E) or caveolae pathway inhibitor Methyl β-cyclodextrin (C, F) for 1 h. Confluent hBMEC monolayers were infected with exponentially grown SPN at MOI 10 and adherence and invasion assays were performed as described in methods. The levels of invasion or adherence were normalized to vehicle treated cells. Data are represented as mean ± SD of triplicate experiments and representative graphs are shown. Statistical tests were performed using One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. ns, non-significant; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.