FIG 1.
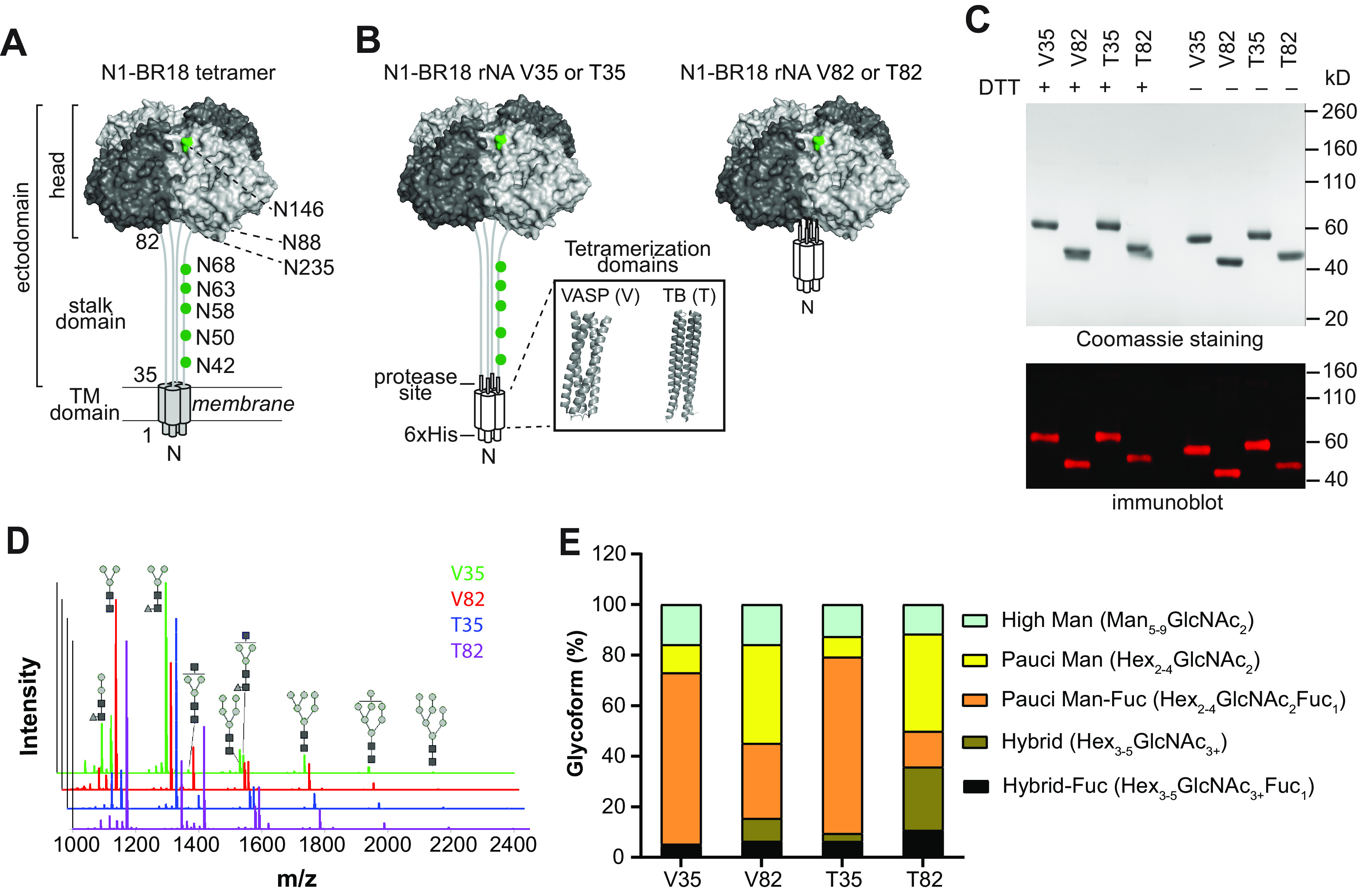
Characterization of N1-BR18 rNAs. (A) Schematic diagram of full-length N1-BR18 showing the transmembrane (TM) domain and the ectodomain, which includes the NA head and stalk. Potential N-linked glycosylation sites are labeled (green). Sites 88 and 235 are not visible in the displayed view. (B) Diagrams of the N1-BR18 rNA construct designs. V35 and T35 contain the full ectodomain of N1-BR18 (residues 35 to 469) connected to the tetramerization domain from VASP (V35) or TB (T35). V82 and T82 are designed similarly using the N1-BR18 head domain (residues 82 to 469). Structures of tetramerization domains from VASP (PDB accession number 1USE) and TB (PDB accession number 1FE6) are shown in a box. (C) Representative images of a Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel containing the rNAs (2 μg/lane) and an immunoblot (0.2 μg NA/lane) resolved using an N1-specific mAb. The rNAs were untreated or reduced with DTT prior to resolution by SDS-PAGE. (D) Spectra of PNGase F-released N-linked permethylated glycans from each rNA. Structures of the most abundant glycoforms are shown: mannose (gray circles), N-acetylglucosamine (black squares), and fucose (gray triangles). (E) Graph displaying the abundances of the different glycoform subtypes. Man, mannose; Hex, hexose; GlcNAc, N-acetylglucosamine; Fuc, fucose.
