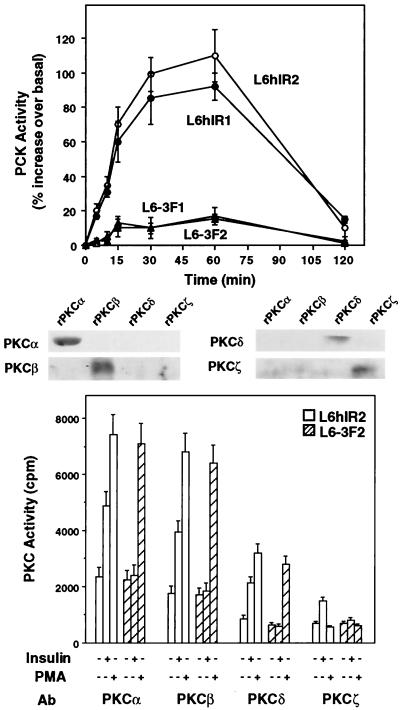
FIG. 1.
Insulin effect on PKC activity in L6 cells. (Top) Cells expressing wild-type human IRs (L6hIR1 and L6hIR2 clones) or kinase-deficient IRs (L6-3F1 and L6-3F2 clones) were exposed to 100 nM insulin for the indicated times. The cells were then solubilized and assayed for PKC activity as described in Materials and Methods. PKC activity is plotted as percent increase above that measured in cells not exposed to insulin. Data points represent the means ± standard deviations of triplicate determinations in four independent experiments. (Bottom) L6hIR2 and L6-3F2 cells were stimulated with insulin for 30 min or PMA for 60 min, solubilized, and immunoprecipitated with isoform-specific PKC antibodies (Ab) (200 μg of protein/sample). PKC activity in the immunoprecipitates was assayed as described in Materials and Methods and is plotted as radioactivity incorporated in the Ac-MBP(4-14) substrate peptide. Bars represent the means ± standard deviations of duplicate determinations in four independent experiments. The specificity of PKC isoform antibodies was controlled by Western blotting recombinant PKCα, -β, -δ, and -ζ (rPKCα, -β, -δ, and -ζ) with the individual antibodies as shown.