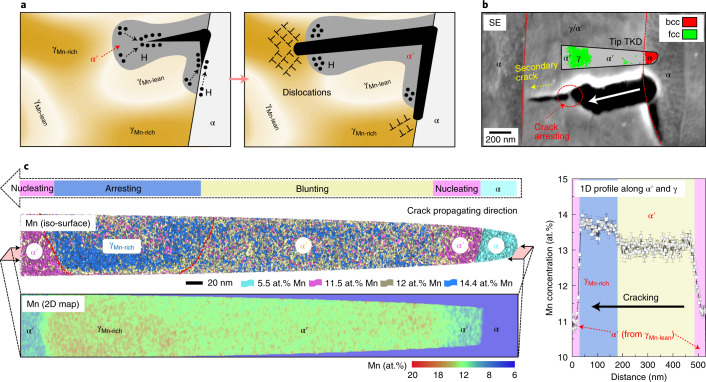
Fig. 4. Chemical-heterogeneity-induced arresting of H-induced cracks.
a, Schematic illustration showing the crack-arresting mechanisms. The stable γMn-rich resists deformation-induced phase transformation, which allows it to blunt and arrest intruding H-induced microcracks owing to the enhanced plastic compliance and reduced H diffusivity therein. b, A representative blunted and arrested H-induced crack in the H-charged and fractured chemical-heterogeneity-manipulated steel (total H amount 6.3 ppmw). The crack was probed by secondary electron (SE) imaging from the area close to the fracture surface and specimen side edge, where H is nearly saturated. The inset is the transmission Kikuchi diffraction (TKD) phase map for the APT tip, which is placed at the region exactly where the tip was lifted out. The red dashed lines mark the interface between ferrite (α) and austenite/martensite (γ/α´). The white arrow indicates the crack propagation direction. c, The APT results for the tip shown in b, containing an iso-composition surface map for Mn, a two-dimensional (2D) Mn concentration map and a one-dimensional (1D) Mn profile across α′ and γ (the error bars represent standard deviations). Colours (pink, yellow, blue) indicate different Mn contents.