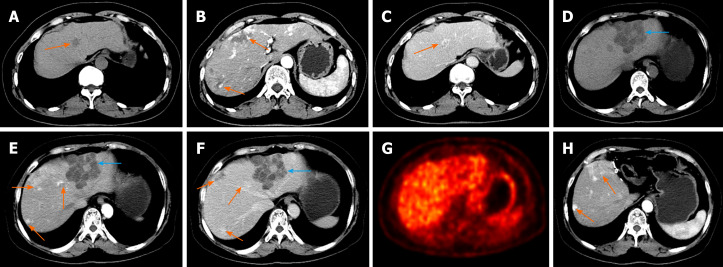
Figure 1.
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) and positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) features of hepatic hemolymphangioma. A–C: CECT images from 3 years ago revealing multiple hepatic hemangiomas (orange arrow) with hypointensity (A) and fast-in and slow-out enhancement patterns (B,C); D–F: CECT before partial hepatectomy presented a new cystic-solid lesion (blue arrow) with multiple internal divisions located in segment II of the liver (D), with delayed CECT enhancement characteristics (E, F); G: PET/CT scan found no significant uptake of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose; H: At 1-year follow up, no obvious recurrent or residual lesion was identified by CT imaging.