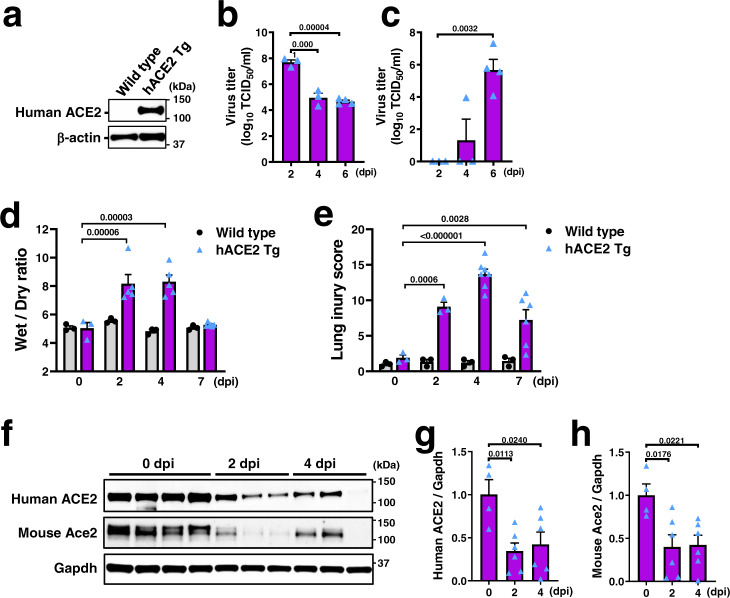
Fig. 5. SARS-CoV-2-induced lung injury and ACE2 downregulation in hACE2 Tg mice.
a Western blot of human ACE2 protein in the lung lysates of uninfected hACE2 Tg mouse expressing human ACE2 under CAG promoter. b–c Virus titers (TCID50) in the lysates of lung (b) and brain (c) prepared from hACE2 Tg mice intratracheally (i.t.) infected with SARS-CoV-2 (2 × 103 TCID50) at 2 dpi (n = 3), 4 dpi (n = 3), and 6 dpi (n = 4). dpi; days post infection. d Lung edema of wild-type and hACE2 Tg mice after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Wet/dry ratio of lung weight of wild type mice (n = 3 each for 0, 2, 4, and 7 dpi) and hACE2 Tg mice (n = 3 for 0 dpi, n = 5 each for 2 and 4 dpi, n = 6 for 7 dpi). e Lung injury score of wild-type and hACE2 Tg mice after SARS-CoV-2 infection. n = 7 for hACE2 Tg mice at 4 dpi, n = 6 for hACE2 Tg mice at 6 dpi, and n = 3 for other experimental groups. f–h Protein expression of human ACE2 and mouse Ace2 in the lungs of SARS-CoV-2-infected hACE2 Tg mice. Representative Western blots are shown (f). Human ACE2 (g) and mouse Ace2 (h) were normalized with Gapdh (n = 4 mice for 2 dpi, n = 6 each for 2 and 4 dpi). All values are means ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (b–e, g, h). Numbers above square brackets show P values. Independent experiments were performed one time (b, c) or two times (a, d–h), and consistent results were obtained.