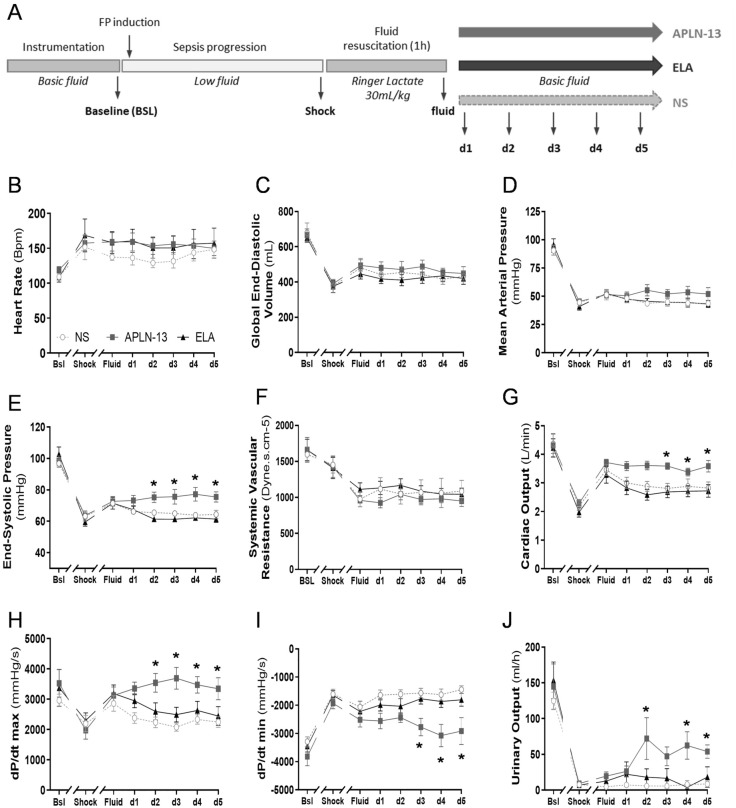
Figure 2.
Apelin-13 (APLN-13) improves cardiorenal axis function in an ovine model of fecal peritonitis (FP). (A) Study Design: Sheep were first prepared as described in Fig. 1. After baseline assessment, fecal peritonitis was induced by intraperitoneal injection of a stool slurry (2 g/kg) and five criteria of shock must be met before fluid resuscitation challenge (RL 30 mL/kg for 1 h) and start of infusions of 20 min-incremental doses of APLN-13 or Elabela (ELA) vs. normal saline (NS), as described in Fig. 1. See “Methods” section for details. Septic shock was achieved 251 ± 15 min after FP induction. (B–I) Heart rate, global end-diastolic volume, mean arterial pressure; end-systolic pressure; systemic vascular resistance; cardiac output, dP/dt max and dP/dt min were assessed by PiCCO-Volef thermodilution or left ventricular catheterization at the baseline (Bsl), shock (Shock), and fluid resuscitation challenge (Fluid) time points and for d1 to d5 corresponding to increasing apelinergic doses. Following fluid resuscitation, APLN-13 maintained cardiac output and increased end-systolic pressure from 0.25 nmol/kg/h. APLN-13 also enhanced dP/dt max along with decreased dP/dt min from 0.25 nmol/kg/h and 2.5 nmol/kg/h, respectively. (J) Urinary output was measured by percutaneous bladder catheterization. APLN-13 increased urinary output from 0.25 nmol/kg/h. All results are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 6/group). Statistical analyses for quantitative variables were performed with a paired Student’s t-test (normally distributed variables). Dose–response and time-course analyses were performed with repeated measures two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. *p < 0.05 vs. normal saline (NS)-infused sheep.