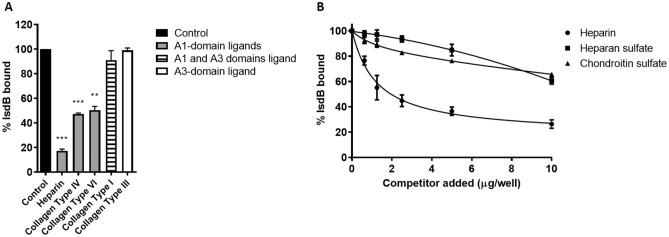
Figure 4.
Interference of vWF ligands with the VWF/IsdB interaction. (A) the effect of vWF ligands on the binding of IsdB NEAT1–NEAT2 to immobilized vWF. Microtiter wells coated with vWF were incubated with IsdB NEAT1–NEAT2 in the presence of the indicated potential competitors. IsdB NEAT1-NEAT2 binding to the wells was detected by the addition of a polyclonal rabbit anti-IsdB IgG followed by HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG. Binding data are expressed as a percentage of the control, i.e. incubation performed in the absence of any potential IsdB competitor. Statistically significant differences are indicated (**, P < 0.01, ***, P < 0.001). (B) The effect of polyanionic compounds on the binding of IsdB NEAT1–NEAT2 to immobilized vWF. Microtiter wells coated with vWF were incubated with IsdB NEAT1–NEAT2 in the presence of increasing concentrations of heparin, heparan sulfate, and chondroitin sulfate. Binding was detected as reported in (A). The data points are the means ± SD from three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate.