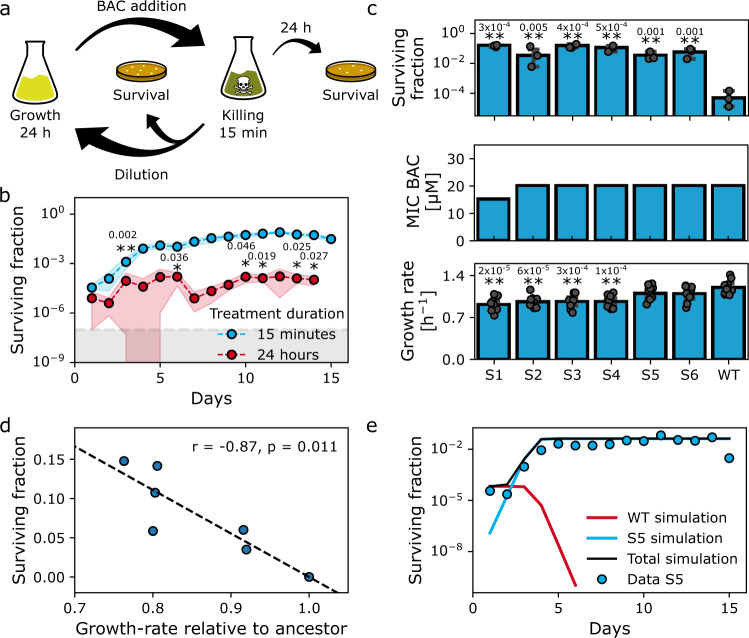
Fig. 2. Periodic failure of disinfection rapidly selects for tolerance against BAC.
a Schematic of the evolution experiment selecting for the survival of BAC disinfection. b Daily exposure to BAC rapidly selects for tolerance. Shown are the geometric means ± 95% C.I., n = 6 biological replicates. The first round that is significantly different from the beginning of the treatment is marked by asterisks. p < 0.05; p < 0.01 (two-tailed paired t-test of log-transformed survival fractions). c Phenotypic characterization of six evolved clones. The surviving fraction of the evolved clones after 20 min of BAC treatment is increased (n = 3 biological replicates). Significance of difference to wild-type indicated by asterisks: p < 0.05; p < 0.01 (two-tailed t-test of log-transformed survival fraction). The MIC against BAC is not affected in the evolved clones (n = 4 biological replicates). The growth rate of the evolved clones is reduced, signifying the cost of tolerance (n = 10 biological replicates). Significance of difference to wild-type indicated by asterisks: p < 0.05; p < 0.01 (two-tailed unpaired t-test of growth rates). Error bars show 95% confidence intervals. For the surviving fraction, the geometric mean is reported. For the growth rate, the arithmetic mean is reported. For the MIC, the maximal value from four biological replicates is reported. d Trade-off between tolerance and growth rate in individual clones. Significance of correlation: two-sided test with t-distribution of the test statistic. The data are taken from panel (c). e Population dynamics can be explained by trade-off between growth-rate and tolerance of individual clones. Simulations of survival fraction during the serial passage experiment with alternating growth and kill cycles (lines) quantitatively reproduce the experimental data (circles). The parameters for growth rate and survival fraction are the same as for clone S5 in panel (c). Simulations of all individual clones can be found in Fig. S3. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. Exact p-values are indicated above the asterisks.