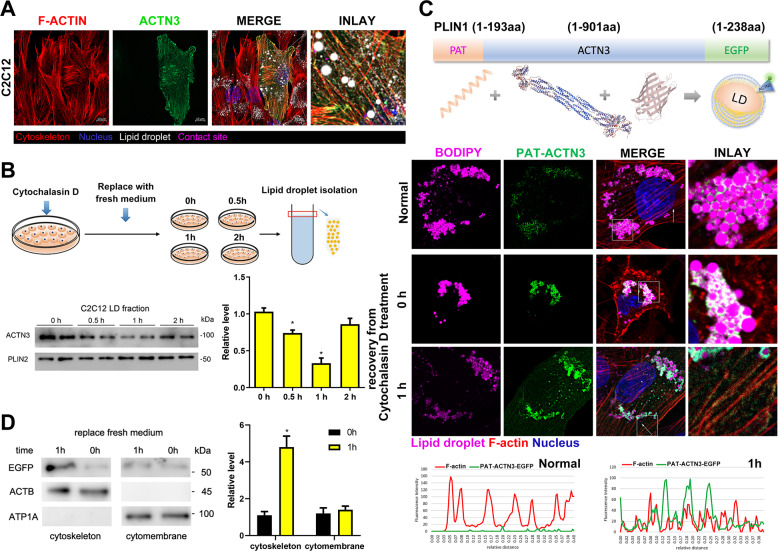
Fig. 5. Transfer of actinin from LD surface to microfilament during microfilament remodeling.
A Co-localization of ACTN3, microfilaments, and LDs in C2C12 cells. B The C2C12 cells were treated with cytochalasin D for 2 h. Then, the medium was replaced with a fresh medium. The LDs were isolated at 0 h, 0.5 h, 1 h, and 2 h, respectively. The ACTN3 levels were detected by Western blotting. C The LD-targeting ACTN3 plasmid was constructed by inserting a PAT domain (PLIN1 1–193aa) at the N-terminus of ACTN3. The co-localization of PAT-ACTN3-EGFP, LDs, and microfilaments in C2C12 cells was detected by a co-confocal microscope. The fluorescence intensity, along with the arrow line, is plotted in the below graphs. D The C2C12 cells (expressing PAT-ACTN3-EGFP) were treated with cytochalasin D for 2 h, then the medium was replaced with a fresh medium. The subcellular components were isolated at 0 and 1 h, respectively. The levels of EGFP were detected. ACTB was utilized as the microfilament reference protein and ATP1A was utilized as cytomembrane reference protein. *p < 0.05. Results are from three technical repeats (N = 3) for a representative of three biological repeats (N = 3).