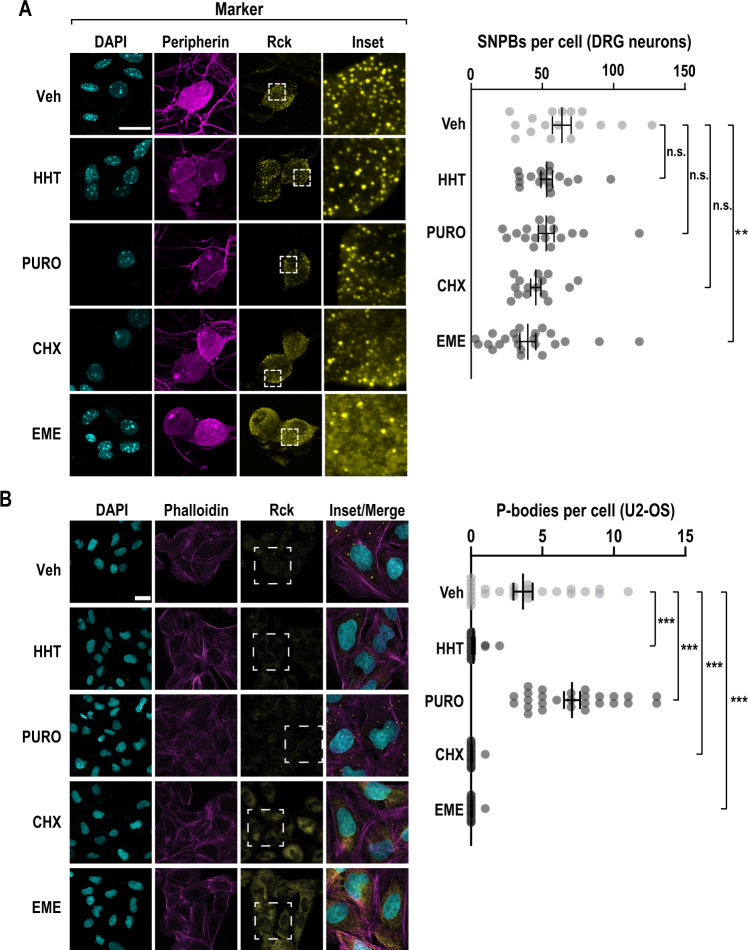
Fig. 1. The translation inhibitor emetine reduces p-bodies in primary sensory neurons.
A Primary DRG cultures were treated with vehicle (Veh), homoharringtonine (HHT, 50 µM), puromycin (PURO, 10 µM), cycloheximide (CHX, 20 µg/ml), or emetine (EME, 50 µM) for a period of 1 h and subjected to ICC. Confocal imaging was used to identify p-bodies and key markers. DRG neurons were identified by peripherin immunofluorescence (magenta) and SNPBs were identified based on Rck (yellow). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (cyan). A left Representative confocal images. Scale bar = 20 µm. A right Quantification of p-bodies in primary DRG neurons. The error bars represent mean ± S.E.M. For Veh, HHT, PURO, CHX, and EME n = 17, 17, 17, 15, and 23 cells, respectively p-values determined by one-way ANOVA. Veh vs EME p = 0.0076. B U2-OS cells were subjected to the same treatments as in A and subjected to ICC. Cells were labeled with phalloidin-TRITC (magenta) and Rck used as a marker for p-bodies (yellow). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (cyan). B left Representative confocal images. Scale bar = 30 µm. B right Quantification of p-bodies per cell. The error bars correspond to the mean ± S.E.M. For Veh, HHT, PURO, CHX, and EME, n = 25, 24, 27, 28, and 29 cells, respectively p-values determined by one-way ANOVA. Veh vs. HHT p < 0.0001, Veh vs. PURO p < 0.0001, Veh vs. CHX p < 0.0001, Veh vs. EME p < 0.0001. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.