Figure 1.
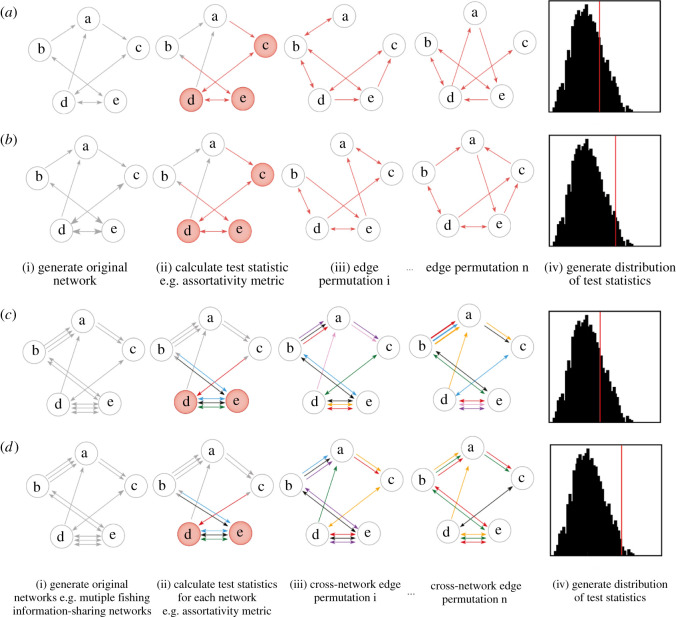
Schematic representation of edge-based permutation models with directed network data. Four main null model steps include (i) creating a social network from the observed data, (ii) calculating a test statistic, for example, a network-level metric like degree assortativity (high-degree fishers that are coloured red primarily connect to other high-degree fishers), (iii) randomizing the observation data (typically with 1000 permutations) and (iv) recording the distribution of possible test statistics. Conclusions can then by drawn by comparing the observed test statistics with the distribution test statistics, and the p-value calculated. Throughout the edge permutations, the fisher positions remain the same, but the configuration of edges between fishers change based on select criteria. The four null model examples shown are all used in this paper's analysis. (a) Outgoing edge permutation allows the randomization of all incoming links, while maintaining the number of nominations (outgoing links) each individual made, (b) edge permutation only allows the swap of links, by maintaining the number of nominees (incoming links) and nominations (outgoing links) each individual made in this information-sharing network. (c) Network swap permutation maintains each dyadic nomination, but randomizes the networks that these nominations were made in (i.e. when individual X nominated individual Y for information sharing within three different information-sharing networks (represented by different coloured arrows), the cross-network permutation allows these three nominations to be reassigned to any of the nine possible networks), and (d) conservative network swap permutation maintains each dyadic nomination, but randomizes the networks that these nominations were made in, while also controlling for the number of nominations that took place overall within each network (i.e. when individual X nominated individual Y for information sharing within three different information-sharing networks, these three nominations were reassigned among the networks in a way that was equal to the number of nominations in each network).