Figure 4.
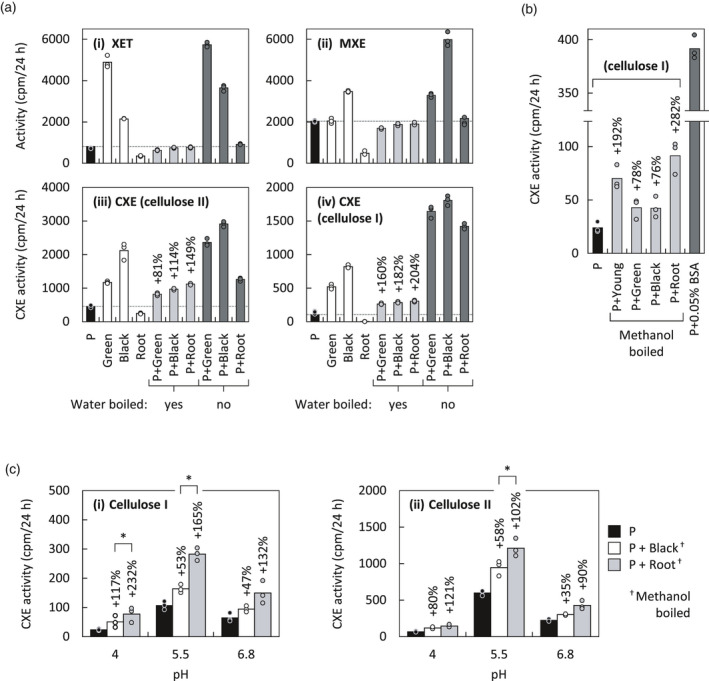
Stimulatory effect of non‐enzymatic Equisetum polymers.
Acceptor substrate in all cases: [3H]XXXGol.
(a) Effect of Equisetum extracts on activities of Pichia‐produced EfHTG. Donor substrates: (i) XyG, (ii) MLG, (iii) cellulose II, (iv) cellulose I, for detection of XET, MXE, CXE and CXE activities, respectively. Enzymes (x‐axis): Green, from green shoot middle; Black, from blackish shoot base; Root, from roots; P, Pichia‐produced EfHTG; and combinations thereof. ‘Boiled’ indicates that the Equisetum enzyme extracts (Green, Black, Root), but not the P, had been pre‐incubated in aqueous solution at 100°C for 5 sec, which is expected to denature EfHTG and XTHs but not expansins (Wang et al., 2014) or the XTH‐activating factor (XAF) of Nguyen‐Phan and Fry (2019). Stimulating effects of ‘boiled’ Equisetum extracts on CXE activities are indicated as a percentage above columns. Dashed lines indicate activities of Pichia‐produced EfHTG only; n = 3; data points are shown as circles.
(b) CXE activity of Pichia‐produced EfHTG in the presence of activity‐stimulating Equisetum crude extracts that had been boiled in methanol (common procedure to maintain expansins but not enzymes active). For comparison, CXE activity on NaOH‐pre‐treated paper and in presence of 0.05% BSA is shown (dark grey column); n = 3; data points are shown as circles. Designation of extracts is as in (a), plus ‘Young’ = from green shot top.
(c) Same experiment as in (b), but performed at three different pH values and in presence of 3% (w/v) BSA. Methanol‐boiled extracts from the blackish shoot base and roots were used. Statistically significant differences between CXE activity stimulations by extracts from roots or blackish shoot bases (determined by standard t‐tests) are indicated by asterisks; n = 3; data points are shown as circles, P < 0.05.
Cellulose I, plain Whatman No. 1 paper; cellulose II, alkali‐treated Whatman No. 1 paper.
