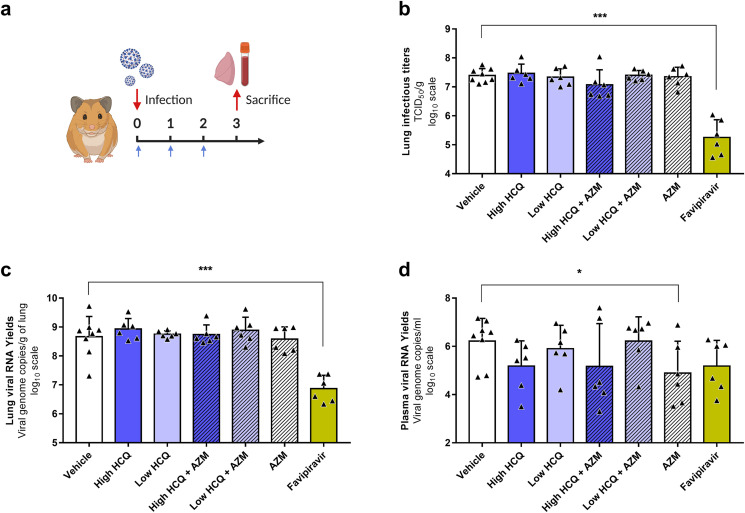
Fig. 2.
Antiviral activity of HCQ and AZM alone or combined in a Syrian hamster model at 3 dpi.
(a) Experimental timeline (realized on biorender.com). Groups of 6 or 8 hamsters were intranasally infected with 1 × 104 TCID50 of SARS-CoV-2, treated from 0 to 2 dpi (blue arrows) and sacrificed at 3 dpi. (b) Lung infectious titers measured using a TCID50 assay. (c–d) Lung viral RNA yields (c) and plasma viral loads (d) measured using a RT-qPCR assay. Data represent mean ± SD of individual data of hamsters (n = 6 to 8; details in Supplemental Table 4). *** and * symbols indicate that lung infectious titers, lung viral RNA yields or plasma viral loads are significantly smaller than those for the untreated group (vehicle) with a p-value ranging between 0.0001-0.001 and 0.01–0.05, respectively (Unpaired and Welch's t tests). Clinical follow-up of this experiment is presented in Supplemental Fig. 3.