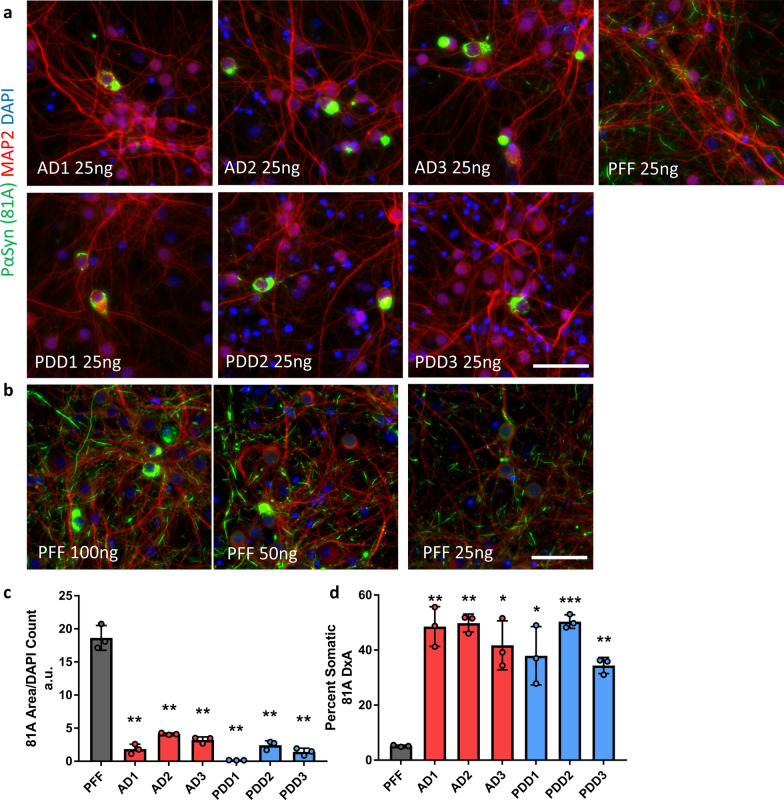
Fig. 2.
Patient-derived, insoluble α-Syn species are active in cultured mouse hippocampal neurons and induce distinct α-Syn pathology. a Primary hippocampal neurons were treated in 96 well plates at DIV 7 for 14 days with 25 ng of PFF, AD or PDD α-Syn. AD and PDD α-Syn induced somatic aggregates in neuronal cell bodies and some thread like neuritic aggregates whereas human α-synuclein PFF’s induced predominantly neuritic aggregates. DAPI and MAP2 were used to show nuclei and somatodendritic area. Scale bars 50 µm. b Neurons were treated in 96 well plates at DIV 7 for 14 days with increasing amounts (25, 50, 100 ng) of human PFF. The number of somatic aggregates increased with higher concentrations of human PFFs, but neuritic pathology also increased. Scale bar 50 µm. c Quantification of total 81A pathological area in neurons treated in 96 well plates with 25 ng per well AD, PDD, or PFF α-Syn. d Percent of total 81A pathology in somatic inclusions from neurons treated as in c. Totals are the average of 3 replicate wells. Error bars represent the standard deviation. Significance compared to PFF treated neurons was determined by student t-test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001)