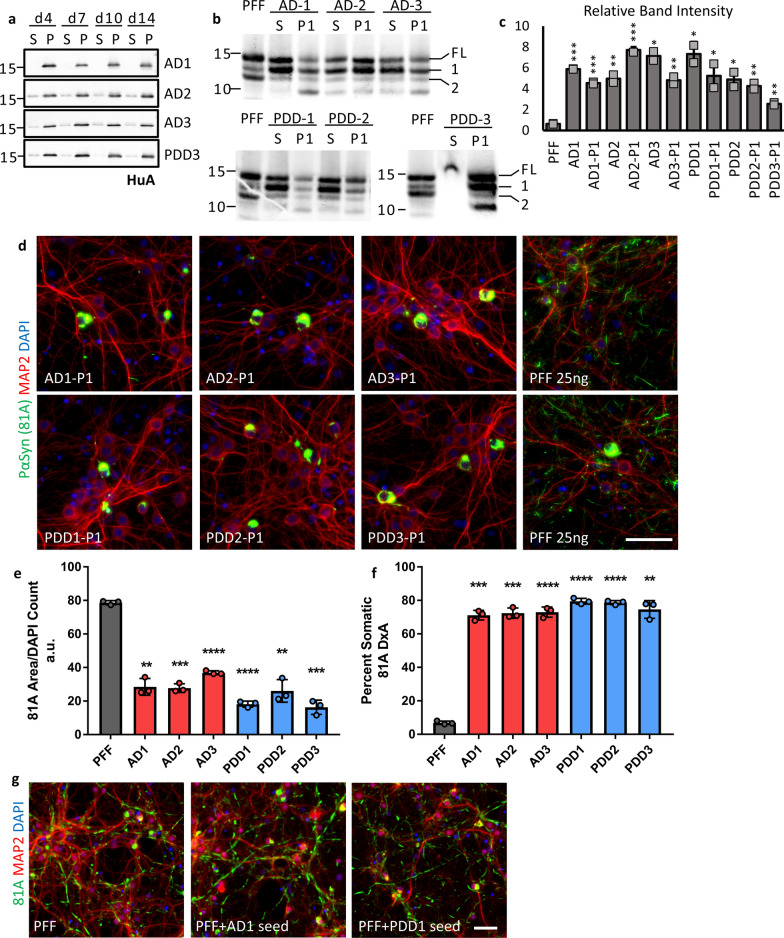
Fig. 3.
In vitro amplification of patient LB α-Syn preserves characteristic pathological phenotype of the original material. a Aggregation of recombinant monomer seeded with 5% patient LB α-Syn was monitored by sedimentation. Aliquots were taken from aggregation reactions at 4, 7, 10, and 14 days and centrifuged at 100 k x g for 30 min at room temperature. Supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions were analyzed by Western blot. Membranes were probed with HuA. b 300 ng of LB seeds (S) or LB-P1 (P1) was partially digested with 0.25 ug of Proteinase K (PK) for 10 min at 37 °C. The resulting PK resistant bands were analyzed by Western blot. Membranes were probed with HuA. Major bands labelled full-length (FL), first fragment (1), and second fragment (2). The level of contaminant protein in PDD3 inhibited digestion of the seed sample. c Band intensity for fragments 1 and 2 were quantified and relative intensity of fragment 1 to fragment 2 was plotted for each sample to highlight the banding pattern. Values are the average of two independent digestions. d Mouse hippocampal neurons were treated in 96-well plates with 25 ng of α-Syn PFF or LB-P1 at DIV 7 for 14 days. 81A positive pathology induced by LB-P1 is consistent with LB seeds pathology. Scale bar 50 µm. e Quantitation of total 81A area for neurons treated as in d. f Percent of total 81A pathology in somatic inclusions from neurons treated as in d. Totals are the average of 3 replicate wells. g Mouse hippocampal neurons treated in 96 well plates with 25 ng of PFF or 95 ng PFF pre-incubated with 5 ng LB seeds to demonstrate that addition of LB seeds to PFF does not induce primarily cell body inclusions. PFF + seed samples were incubated the same as for P1 reactions. Scale bar 50 µm. All error bars represent the standard deviation. Significance compared to PFF was determined by student’s t-test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001)