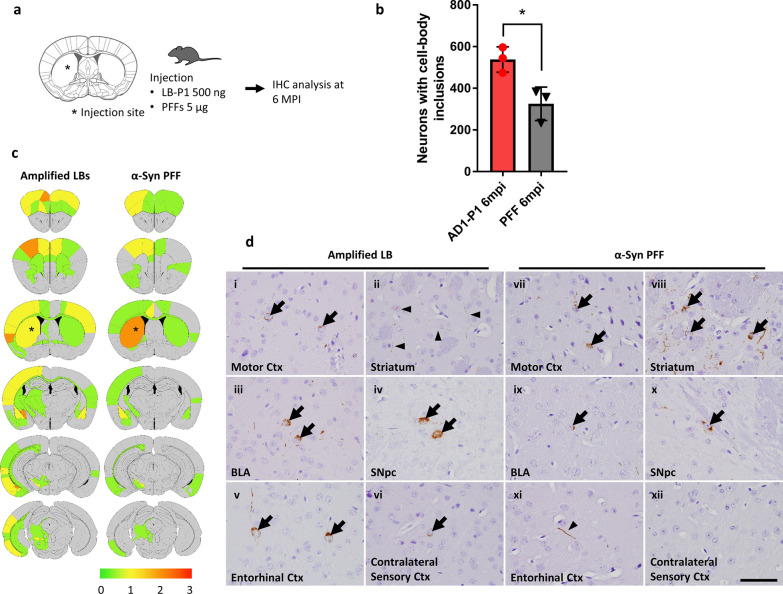
Fig. 4.
Injection of amplified LB-P1 into WT mice induces altered pathological spread compared to PFF. a Schematic representation of experimental design. WT mice were injected with 500 ng of LB-P1 or 5 μg of human α-Syn PFF into the dorsal striatum and analyzed by immunohistochemistry (IHC) at 6 months post-injection (mpi). b Quantitation of neuronal inclusion in whole brains of mice injected with LB-P1 or PFF and sacrificed 6 mpi. Totals are the average of 3 animals. Error bars represent the standard deviation. Significance compared to PFF injected animals was determined by student t-test (*p < 0.05). c Distribution of Pα-Syn pathology 6 mpi. Heat map colors represent the extent of pathology by semi-quantitative analysis (light yellow: mild pathology, yellow: moderate pathology, orange: severe pathology, red: very severe pathology). d Representative Pα-Syn immuno-histochemistry in the motor cortex (Ctx), striatum, basolateral amygdala (BLA), substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc), entorhinal Ctx, and contralateral sensory Ctx in LBP1-injected (i–vi) and PFF–injected (vii–xii) mouse 6 mpi. Arrows indicate Pα-Syn positive, somatic inclusions. Arrowheads indicate Pα-Syn positive, neuritic inclusions. Scale bar 50 µm