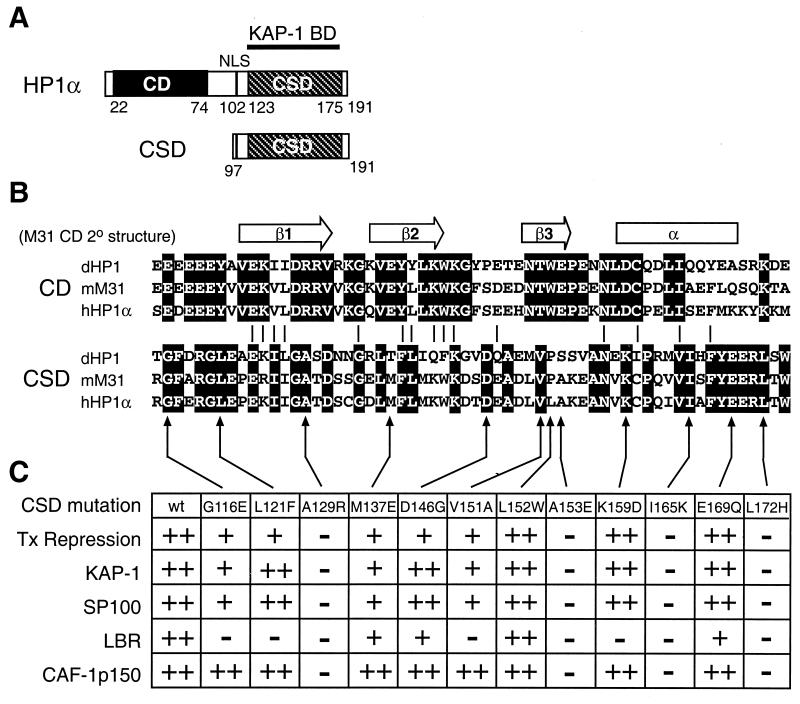
FIG. 2.
Schematic representations of the HP1 protein, the CD, and the CSD. (A) Diagram of human HP1α depicting the prototypical structure of the HP1 proteins. The relevant domains are noted; NLS, nuclear localization signal. The CSD polypeptide fragment from human HP1α is shown. BD, binding domain. (B) Alignment of the primary amino acid sequences of the CD and the CSD of D. melanogaster HP1 (dHP1), mouse M31 (mM31), and human HP1α (hHP1α) proteins. The secondary structure determined for the CD of M31 is indicated above. Identical residues within either the CD or the CSD are highlighted in black. (C) Point mutations engineered in the human HP1α CSD. The table summarizes the transcription (Tx) repression activity of the mutant CSD polypeptides and their ability to bind to various HP1 partner proteins. The reported values were judged relative to the activity observed for the wild-type (wt) CSD: ++, 100 to 75%; +, 75 to 25%; −, 25 to 0.