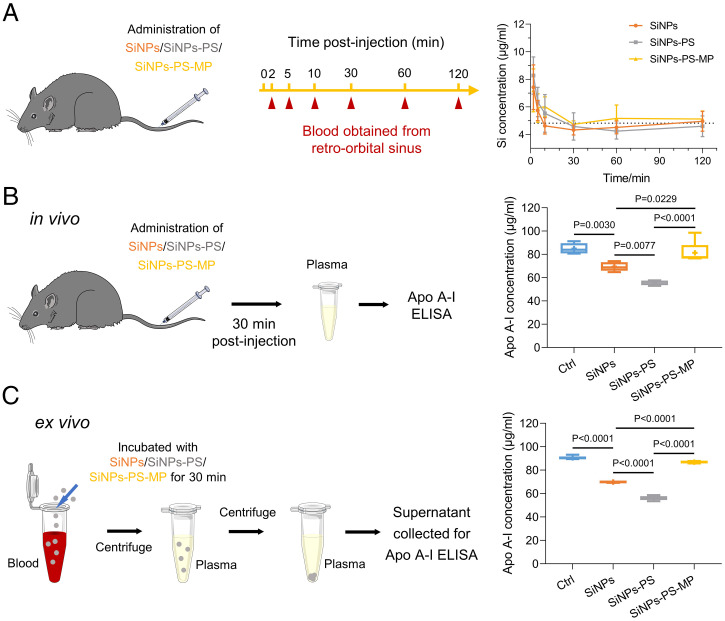
Fig. 4.
SiNPs exposure induces Apo A-I depletion in blood. (A) SiNPs, SiNPs-PS, and SiNPs-PS-MP clearance from the circulation. Male C57BL/6 mice were intravenously injected with SiNPs, SiNPs-PS, and SiNPs-PS-MP (250 μg), respectively. The mice blood was collected from retro-orbital sinus at different time points for Si element analysis by ICP-OES. Si concentration of blank mice blood was presented as dashed line. Data were represented as the mean ± SD (n = 5). (B) SiNPs and SiNPs-PS exposure induced in vivo Apo A-I depletion. Male C57BL/6 mice received intravenous injection of saline, SiNPs, SiNPs-PS (500 μg, calculated by the mass of SiNPs), and SiNPs-PS-MP, respectively. The mice were euthanized 30 min postinjection, and the concentration of Apo A-I in MP was determined. Data were represented as the mean ± SD (n = 5). (C) SiNPs-induced ex vivo Apo A-I depletion. The whole blood of mice was collected and pooled. SiNPs, SiNPs-PS, and SiNPs-PS-MP (500 μg SiNPs/mL blood) were added. The mixture was incubated at 37 °C for 30 min. Blood was centrifuged at 800 g for 10 min to obtain plasma, then centrifuged at 30,000 g for 15 min to separate SiNPs. The supernatant was collected for Apo A-I determination (n = 5).