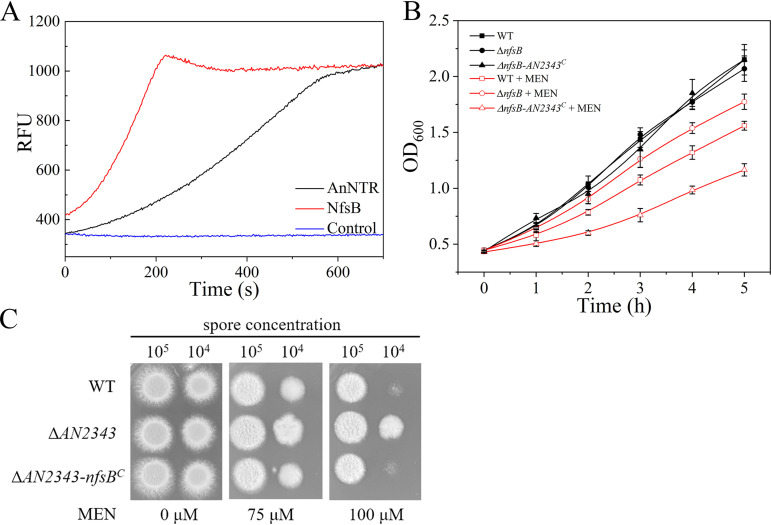
FIG 4.
Deleterious effect of NfsB on menadione detoxification in E. coli. (A) Comparison of the efficiency of O2•− generation catalyzed by A. nidulans and E. coli NTRs. The reaction mixture was the same as that described in Fig. 3A. The reaction was initiated by the addition of 3.6 μM AnNTR or NfsB, respectively. (B) NTRs from either E. coli or A. nidulans promotes E. coli sensitivity to menadione. For the phenotype analysis, E. coli-WT (wild-type E. coli) and ΔnfsB (E. coli nfsB disruption) strains were transformed with empty pET32a. The ΔnfsB-AN2343C strain was constructed by introducing the pET32a-AnNTR plasmid into ΔnfsB (cross-species complemented with AN2343 in ΔnfsB). After induction for 4 h, both strains were diluted to the same concentrations (OD = 0.45) with Luria-Bertani medium (LB) containing 0.8 mM IPTG. Growth curves of both strains in LB with or without 0.3 mM menadione (MEN) were recorded at 1 h intervals at OD600. (C) Expression of NfsB in A. nidulans ΔAN2343 restored its sensitivity to menadione. Conidia from the WT, ΔAN2343, and ΔAN2343-nfsBC (cross-species complementation of E. coli nfsB gene in ΔAN2343) strains with serial dilutions were spotted on minimal media plates with or without the indicated concentrations of menadione, followed by incubation at 37°C for 48 h. The data are the means ± the SD of three independent experiments.