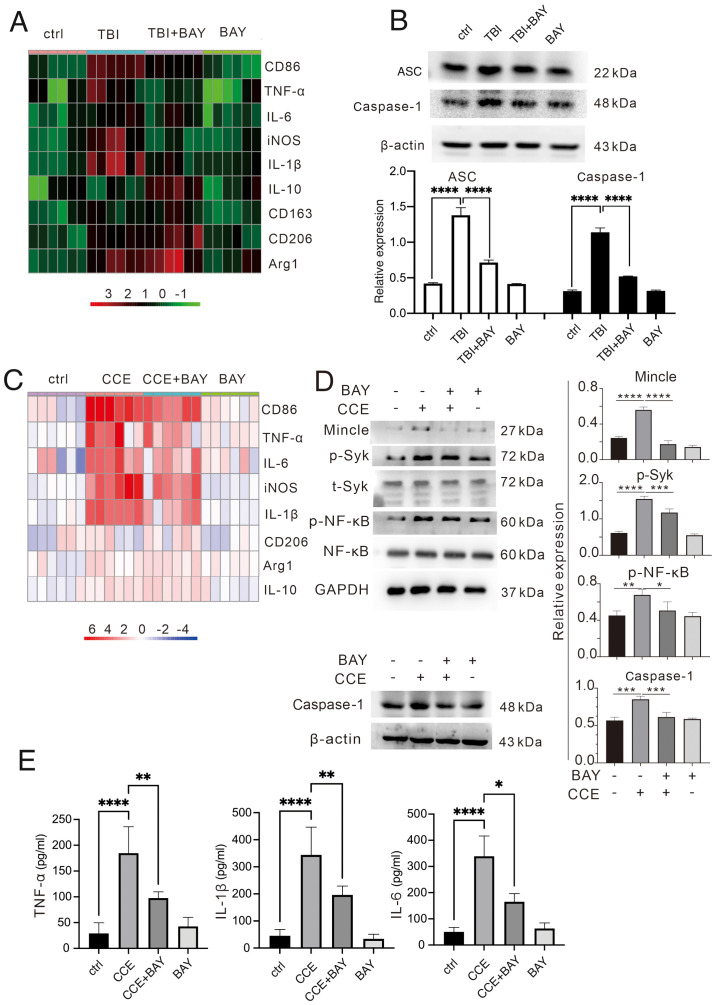
Figure 2.
BAY can modulate the immunological function of microglia after TBI insult. (A) Inflammatory factors (CD86, TNF-α, IL-6, iNOS, IL-1β, IL-10, CD163, CD206 and Arg1) in mouse brain tissues after TBI were measured using RT-qPCR. (B) Expression levels of ASC and caspase-1 proteins in vivo were determined via western blotting. (C) Inflammatory factors (CD86, TNF-α, IL-6, iNOS, IL-1β, IL-10, CD163, CD206 and Arg1) in microglial cells treated with CCE were measured using RT-qPCR. (D) Expression levels of caspase-1 and proteins in the Mincle/Syk/NF-κB signaling pathway associate proteins (Mincle, p-Syk, t-Syk, p-NF-κB and NF-κB) in vitro were determined via western blotting. (E) Production of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in the supernatant of microglia treated with CCE was determined using ELISA. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001. BAY, BAY61-3606; TBI, traumatic brain injury; CCE: cerebral cortex extract; Mincle, macrophage-inducible C-type lectin; Syk, spleen tyrosine kinase; p, phosphorylated; t, total; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; Arg1, arginase-1; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR.