Figure 5.
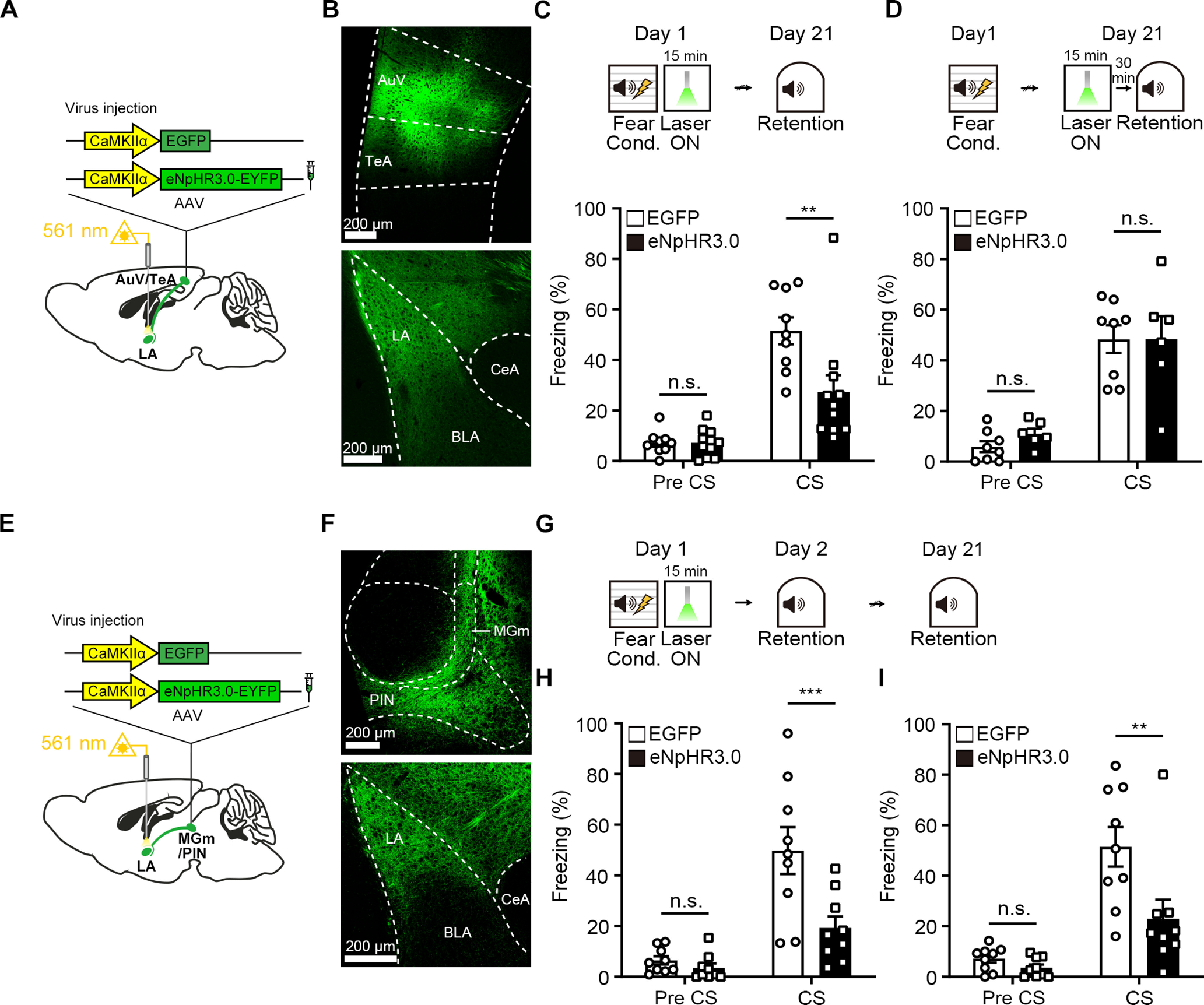
Post-training selective inhibition of cortical input to the LA impairs remote fear memory. A, Schematic depiction of AAV virus injection for eNpHR3.0-EYFP or EGFP expression in the AuV/TeA. B, Representative confocal microscopic images showing expression of eNpHR3.0-EYFP in the AuV/TeA neurons and their terminals in the LA. C, Top, Experimental procedure for photoinhibition of cortical input to the LA immediately after FC. Bottom, Percentage of time spent freezing during remote memory retention was reduced by photoinhibition in the eNpHR3.0 (n = 11 mice) compared with the EGFP group (n = 9 mice). D, Top, Experimental procedure for inhibiting cortical input in the LA 30 min before remote auditory fear memory test. Bottom, There was no significant difference in tone-induced freezing level between groups at remote memory test (EGFP, n = 8 mice; eNpHR3.0, n = 6 mice). E, Schematic depiction of AAV virus injection for eNpHR3.0-EYFP or EGFP expression in the MGm/PIN. F, Representative confocal microscopic images showing expression of eNpHR3.0-EYFP in the MGm/PIN neurons and their terminals in the LA. G, Experimental procedure for photoinhibition of thalamic input to the LA immediately after FC. H, Percentage of time spent freezing during recent memory retention was reduced by photoinhibition in the eNpHR3.0 compared with the EGFP group (n = 9 mice per group). I, In the subsequent remote memory test, mice in the eNpHR3.0 group displayed less freezing than mice in the control EGFP group (n = 9 mice per group). Data are mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001. **p < 0.01.
