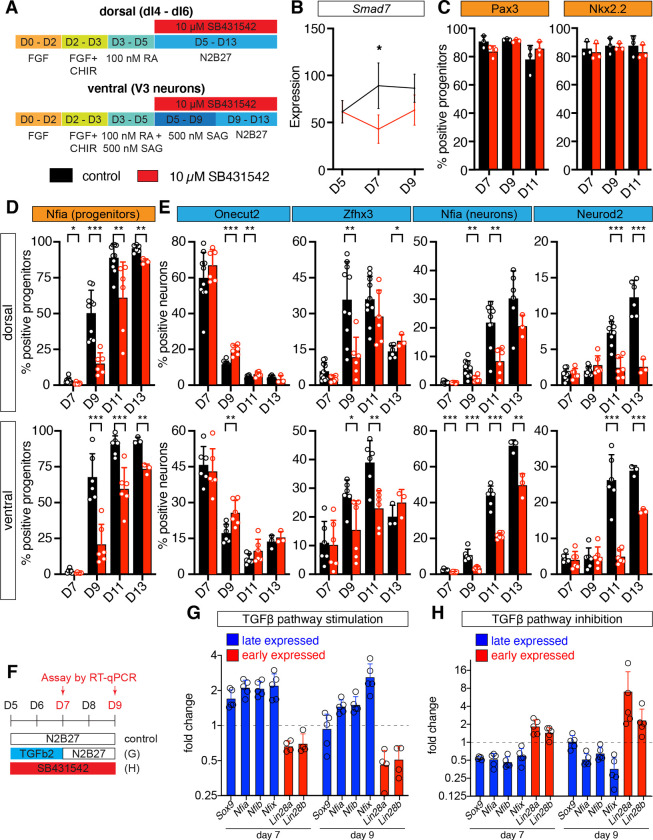
Fig 6. TGFβ signaling influences the timing of temporal TF expression in neurons and progenitors.
(A) Schematics of the differentiation protocols for TGFβ pathway inhibition in dorsal and ventral spinal cord conditions. (B) Inhibition of TGFβ signaling in dorsal spinal cord conditions causes down-regulation of the TGFβ pathway target gene Smad7. (C) TGFβ pathway inhibition does not alter the proportion of progenitors expressing Pax3 in dorsal (left) or Nkx2.2 in ventral (right) conditions. (D) Inhibition of TGFβ signaling delays the induction of Nfia in dorsal and ventral spinal cord neural progenitors. (E) Percentage of neurons expressing the different temporal TFs in the presence and absence of TGFβ pathway inhibition. TGFβ pathway inhibition causes a delay in the induction of the late neuronal markers Zfhx3, Nfia, and Neurod2 in neurons. (F) Scheme outlining the differentiation protocol to assess the role of TGFβ pathway activation and inhibition on the temporal patterning of neural progenitors. (G) TGFβ pathway activation causes an earlier induction of the late markers Sox9, Nfia, Nfib, and Nfix and earlier down-regulation of Lin28a and Lin28b by RT-qPCR. (H) TGFβ pathway inhibition has the opposite effect on the expression of these markers. Underlying flow cytometry data are provided in S3 Data, qPCR data in S4 Data. FGF, fibroblast growth factor; RA, retinoic acid; RT-qPCR, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; SAG, Shh pathway agonist; TF, transcription factor.