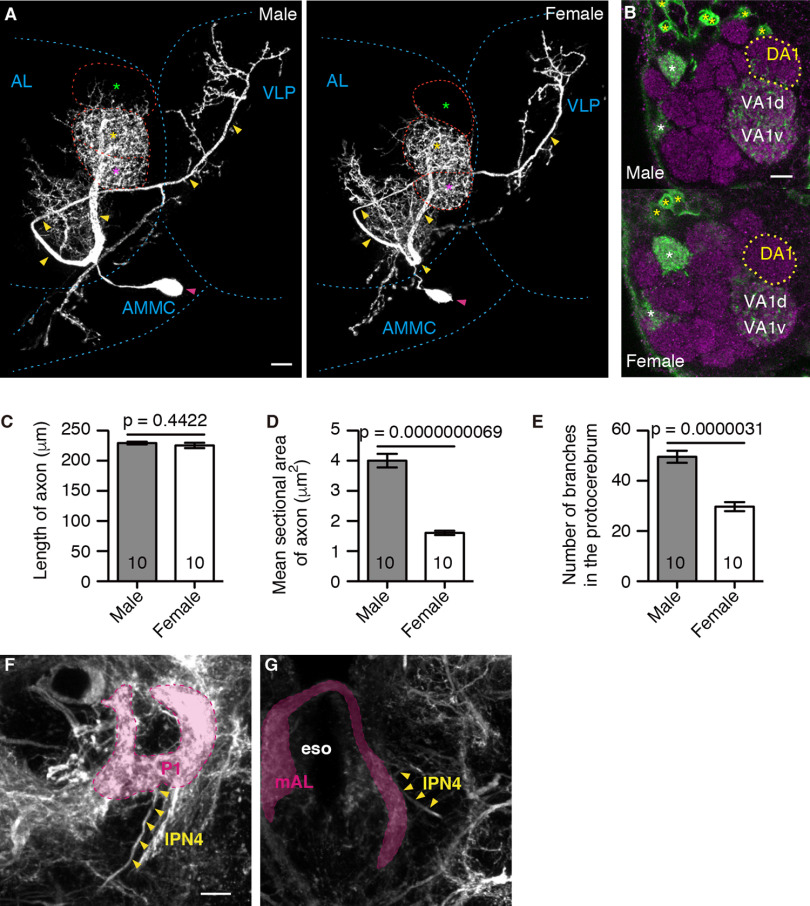
Figure 1.
Sexual dimorphism in the morphology of lPN4 neurons. A, Male (left) and female (right) lPN4s. Primary axons and cell bodies are indicated by yellow and magenta arrowheads, respectively. The DA1 (green asterisks), VA1d (yellow asterisks), and VA1v (magenta asterisks) glomeruli are outlined by red dashed lines. AL, Antennal lobe; AMMC, antennal mechanosensory and motor center; VLP, ventrolateral protocerebrum. B, The innervation of lPN4 (green) into the DA1 glomerulus (yellow dotted lines) in the antennal lobe was observed in males (top), but not in females (bottom). Glomeruli are labeled with the anti-bruchpilot antibodies (magenta). It should be noted that NP6107 also labeled the projection neurons (yellow asterisks) innervating the ordinary glomeruli, DM6, VM7d, and VM7v (white asterisks), which do not respond to fly smells (Seki et al., 2017) and thus do not contribute to the courtship sequence. C–E, Mean length (C) and sectional area (D) of the primary axon, and the number of branches in the protocerebrum (E) of the male and female lPN4s. Comparison between males and females was conducted using two-tailed unpaired t test. Numbers within bars are the numbers of neurons analyzed. Error bars indicate SEM. F, G, The lPN4 axon, indicated by arrowheads, projects to the arborization areas of the P1 neurons (magenta in F) in the VLP and mAL neurons (magenta in G) in the subesophageal zone in the male brain. To label the P1 and mAL neurons in addition to lPN4, we used the fruNP21 GAL4 line, which also labels other neurons. eso, Esophagus. Genotype: NP6107-GAL4 (A, B) or NP21-GAL4 (F, G)/Y or +; 10xUAS-mCD8::GFP/+; 20xUAS-mCD8::GFP/+. Lateral is to the right; dorsal is to the top. Scale bars: A, B, F, 10 μm.