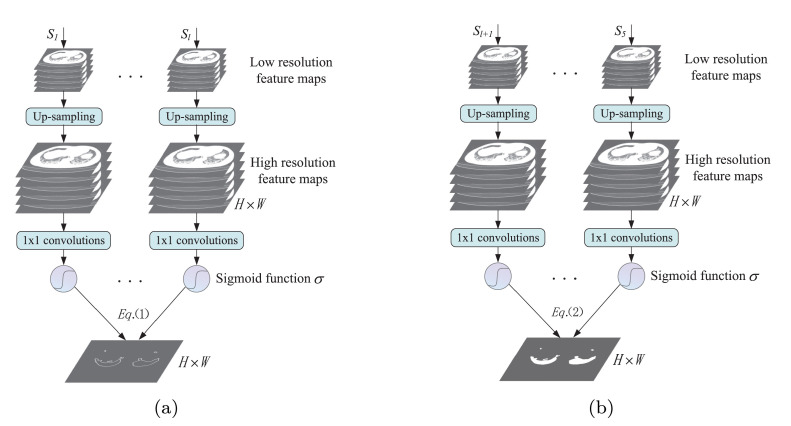
Fig. 3.
An illustration of ESM and ASSM. Firstly, the low resolution feature maps from the stage are resized to the same size with the input image by using bilinear interpolation up-sampling. Then all high resolution feature maps are reduced to a feature map by using convolutions. Finally each pixel value of the obtained feature map is converted to a probability by using Sigmoid function , and the prediction image of the stage is obtained. (a) ESM: the edge supervision is achieved by comparing between the obtained edge prediction image and the corresponding edge Ground Truth (GT) based on Eq.(1). (b) ASSM: the auxiliary semantic supervision is achieved by comparing between the obtained coarse segmented image and the corresponding Ground Truth (GT) of segmentation mask based on Eq.(2).