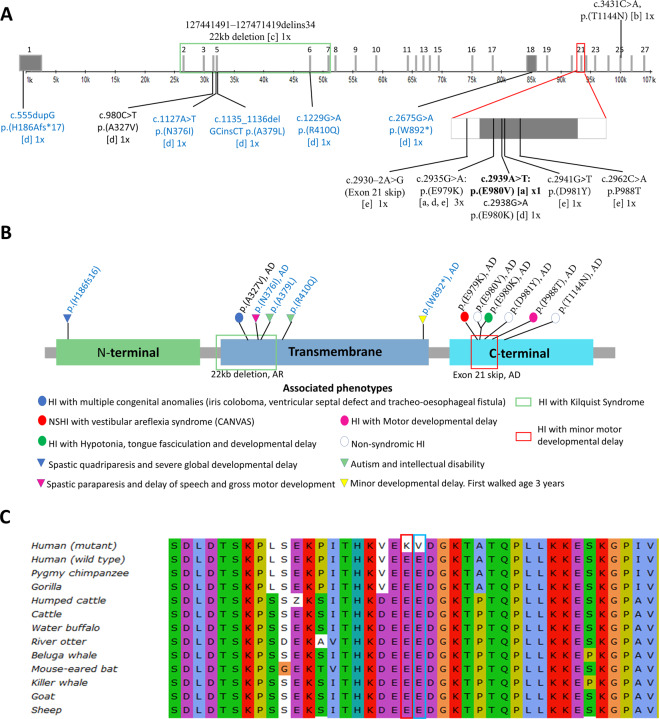
Fig. 2.
Schematic presentation of SLC12A2 gene and protein alignment. A Schematic diagram of HI-associated mutations within the SLC12A2 gene. The variants comprise of those found in our current study[a] and previous studies in cases that present with both syndromic, and non-syndromic hearing loss: Morgan et al. [29][b], Macnamara et al. [27][c], McNeill et al. [25][d], Mutai et al. [24][e]. The number of independent occurrences (1x or 3x) was written beside each variant. The variants that were not associated with HI were written in blue ink. The exons are denoted with a gray bar with the respective exon number on top of each gray bar. B Variants in SLC12A2 protein associated with HI. Circles were used to denote variants associated with HI while triangles were used to represent variants that were not associated with HI. The predominant mode of inheritance was autosomal-dominant (AD), the deletion was autosomal recessive (AR). The mode of inheritance of p.(H196fs16), p.A379L), and p.(R410Q) was not stated by the authors. C SLC12A2 protein sequence alignment. The amino acid position of SLC12A2: p.(E979K) and p.(E980V) are highlighted with red and blue rectangles, respectively