Figure 2. Hypoxia and the integrated stress response (ISR): potential drug targets.
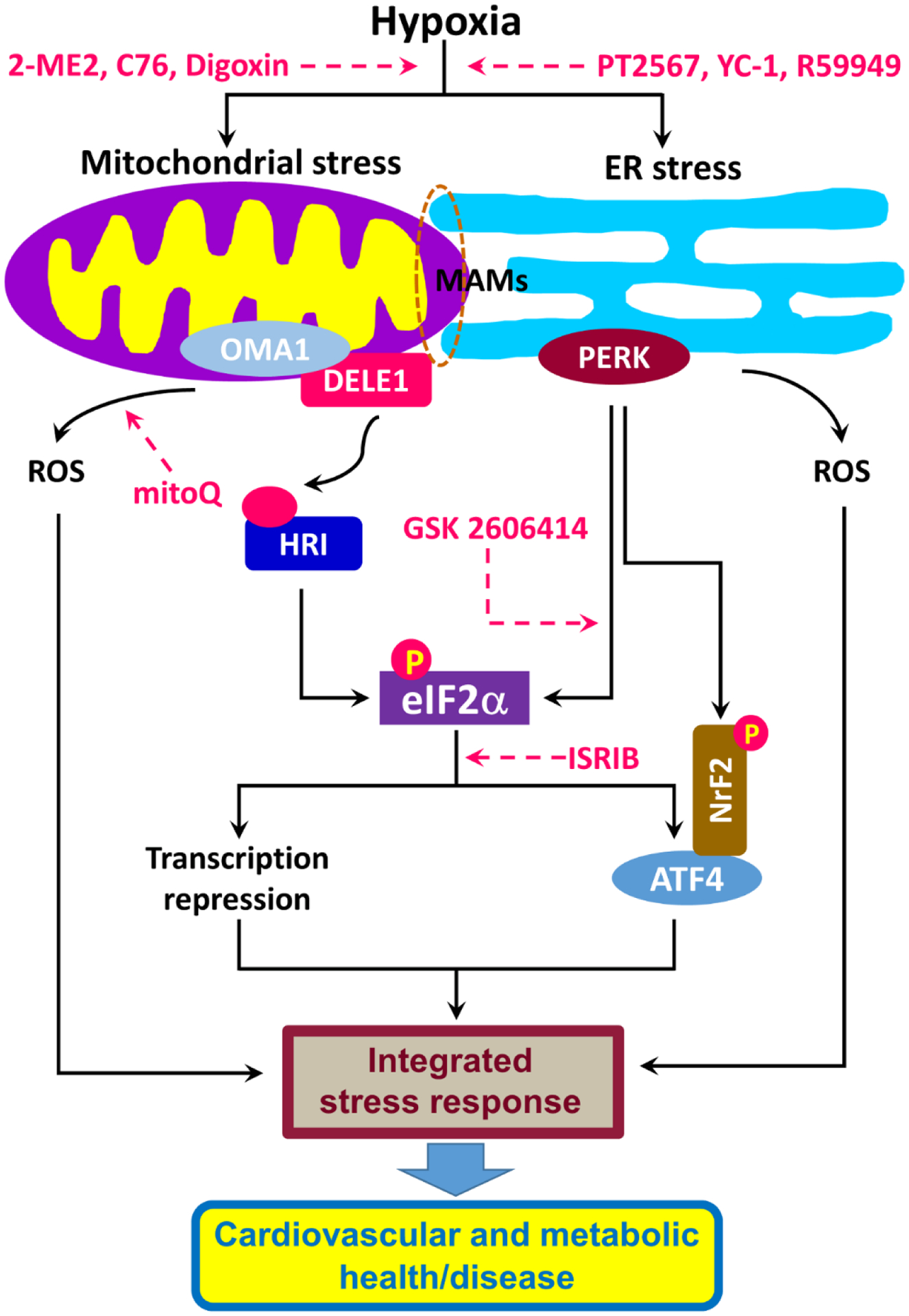
Hypoxia induces mitochondrial stress and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Mitochondrial stress produced via the OMA1-DELE1-HRI pathway and ER stress resulting from the PERK pathway converge at the phosphorylation of eIF2α, leading to changes in the transcription of genes and subsequent cardiovascular and metabolic (mal)adaptations. The ISR can also be activated by oxidative stress resulting from the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Potential targets for drug development are indicated by dashed pink arrows.
Abbreviations: ATF4, activating transcription factor 4; C76, compound 76; DELE1, DAP3-binding cell death enhancer 1; eIF2α, eukaryotic initiation factor 2α; HRI, heme-regulated inhibitor; ISRIB, integrated stress response inhibitor; MAM, mitochondria-associated membrane; ME, 2-methoxyestradiol; mitoQ, mitochondrial-targeted coenzyme Q; NrF2, Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; OMA1, a mitochondrial metallopeptidase encoded by the OMA1 gene; PERK, PKR-like ER kinase 2; YC-1: 3-(5’-hydroxymethyl-2’-furyl)-1-benzylindazole.
