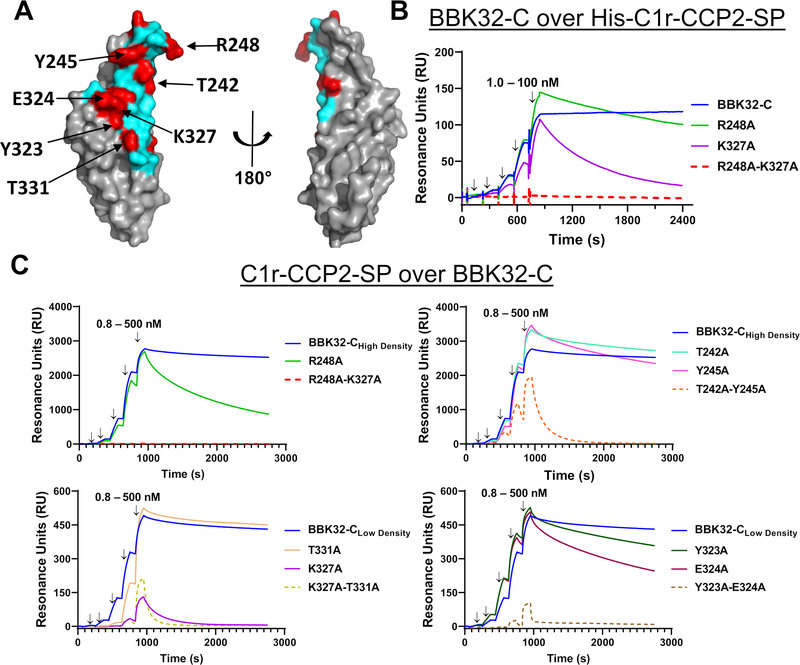
Figure 2. SPR binding assays with structure-guided site-directed BBK32-C mutants.
A) Surface representation of BBK32-C with non-contact surface areas (gray) and BBK32-C/C1r-CCP2-SP contact area (cyan). Residues mutated for this study (red) are indicated in Table 3. Site-directed mutants shown in this figure are denoted with arrows. B) SPR experiments were performed by capturing His-C1r-CCP2-SP on a Ni-NTA sensor chip. BBK32-C and selected site-directed mutants were injected over the His-C1r-CCP2-SP surface in a concentration series (1.0, 3.2, 10.0, 31.6, 100 nM). Injection phases are denoted with arrows. C) SPR experiments were performed in the reverse orientation compared to panel B by immobilizing each BBK32-C protein to sensor chips using amine coupling chemistry. A fivefold concentration series of C1r-CCP2-SP (0.8, 4.0, 20.0, 100, 500 nM) was sequentially injected over each immobilized BBK32-C mutant. Arrows indicate injection phases of each C1r-CCP2-SP concentration. Representative sensorgrams are shown with ligands of similar immobilization density grouped with either high immobilization density BBK32-C (i.e., BBK32-CHigh Density) or low immobilization density BBK32-C (i.e., BBK32-CLow Density). BBK32-C curves are reproduced in each respective panel for comparison. SPR experiments were performed in duplicate. Dissociation constants (KD) were calculated by kinetic fits with a 1:1 Langmuir model (Fig. S2, Table 3). Additional site-directed mutants analyzed by SPR and are shown in Fig. S2.