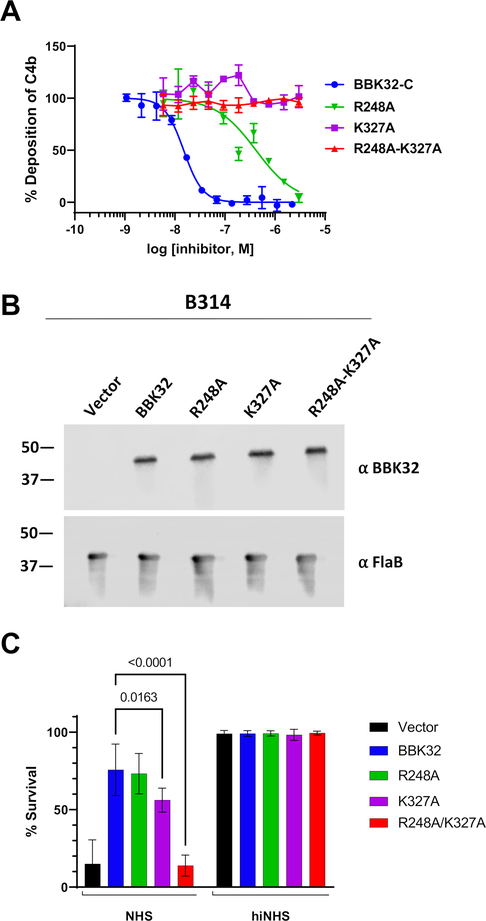
Figure 4. BBK32 R248 and K327 are critical for complement inhibitory activity of BBK32.
A) ELISA-based complement activation assays were performed to determine the ability of BBK32-C mutants to inhibit the classical pathway of complement in vitro. A two-fold concentration series of each BBK32-C mutant was used and performed in duplicate. Inhibitory data for additional site-directed mutants are presented in Figure S6. IC50 values and 95% confidence intervals associated with a normalized four-parameter dose-inhibition fitting procedure are shown in Table 3. B) Western blots of lysates from B. burgdorferi strains B314 containing distinct bbk32 alleles were probed with monoclonal antibodies to BBK32 (α-BBK32) or FlaB (a-FlaB), the latter as a loading control. Vector refers to the plasmid only backbone sample (B314/pBBE22luc), BBK32 is the wildtype bbk32 construct (B314/pCD100), R248A is the bbk32-R248A isolate (B314/pAP5), K327A is the bbk32-K327A isolate (B314/pAP6), and R248A-K327A is the bbk32-R248A-K327A double mutant (B314/pAP7). Numbers on the left refer to the molecular mass of markers (in kDa). C) BBK32 mutant proteins were tested for their ability to confer resistance to normal human serum (NHS). The serum sensitive strain B314 was transformed separately with vector only (black), wildtype bbk32 (blue), bbk32 R248A (green), bbk32 K327A (purple), and bbk32 R248A-K327A (red) and incubated with NHS. Sensitivity was scored as a ratio of the affected cells relative to the total cells viewed via darkfield microscopy. Heat inactivated NHS (hiNHS) was used as a control (right). P-values between bbk32 samples are indicated above. Statistical significance was assessed using a two-way ANOVA.