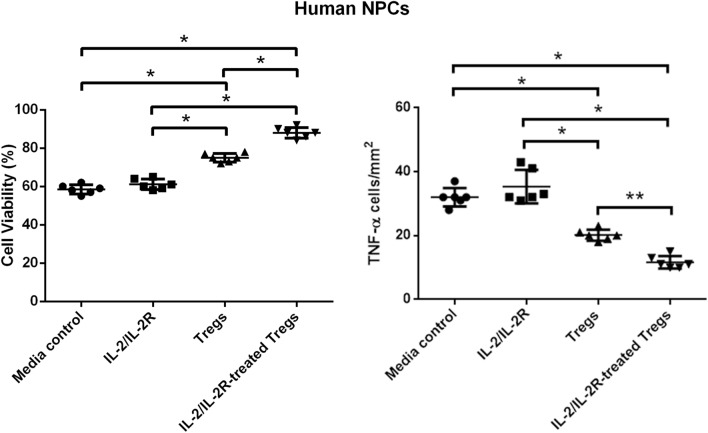
Fig. 4.
IL-2/IL-2R treatment increases Treg-induced survival of NPCs and reduction of inflammation. Left panel: OGD/R reduced cell viability of NPCs but was significantly blocked by IL-2/IL-2R-Treg treatment and Treg treatment (*p < 0.0001), while cell survival with IL-2/IL-2R treatment alone was comparable to that of the media control treatment group (p > 0.05). IL-2/IL-2R-Treg treatment was found to be significantly greater than with Treg treatment alone (*p < 0.0001). Right panel. OGD/R elevated TNF-α levels which was significantly suppressed by IL-2/IL-2R-Treg treatment (*p < 0.0001) or Treg treatment alone (*p < 0.0001), while IL-2/IL-2R treatment alone was ineffective in inhibiting TNF-α levels, comparable to that of the media control treatment group (p > 0.05). TNF-α levels with IL-2/IL-2R-Treg treatment were found to be significantly lower than Treg treatment alone (**p < 0.005). Under ambient condition (i.e., without OGD/R), only trace TNF-α levels were detected