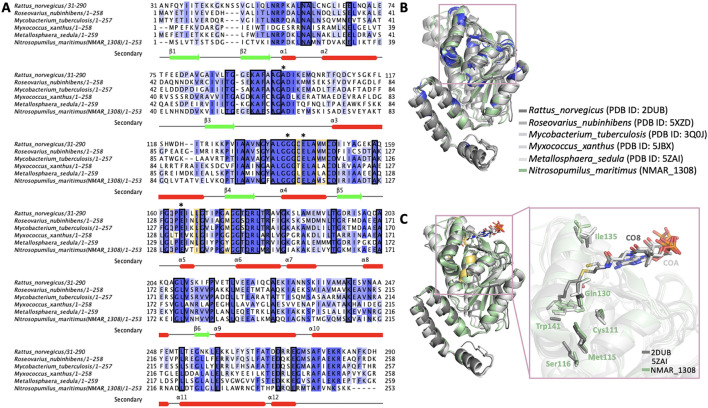
Figure 5.
Overall representation of sequence alignment results. (A) Homologous hydratases (Rattus norvegicus (2DUB), Roseovarius nubinhibens (5XZD), Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (3Q0J)) and dehydratase (Myxococcus xanthus (5JBX)), bifunctional (Metallosphaera sedula (5ZAI)) sequences are aligned to show conserved and critical residues for functioning of Nmar_1308. Black squares represent the conserved residues in the sequence alignment while yellow orange color is used to indicate the observed critical residues. The catalytic residues during hydratase/dehydratase reaction is indicated with asterisks on the top of the sequence. (B) Slate color indicates conserved regions on the structure based on the sequence alignment result in panel A. The detected conserved residues in the hydrophobic binding pocket are shown with a pink square. (C) Residues implicated in the catalysis, Cys111, Met115, Ser116, Gln130, Ile135, and a residue important for limiting substrate size, Trp141, around the hydrophobic binding pocket are shown on the superposed structures of Nmar_1308, Rattus norvegicus hydratase (PDB ID: 2DUB) and bifunctional dehydrate/hydratase from Metallosphaera sedula (PDB ID: 5ZAI). Panel A is generated by Jalview software. Panel B and C are generated by PyMOL (www.schrodinger.com/pymol).