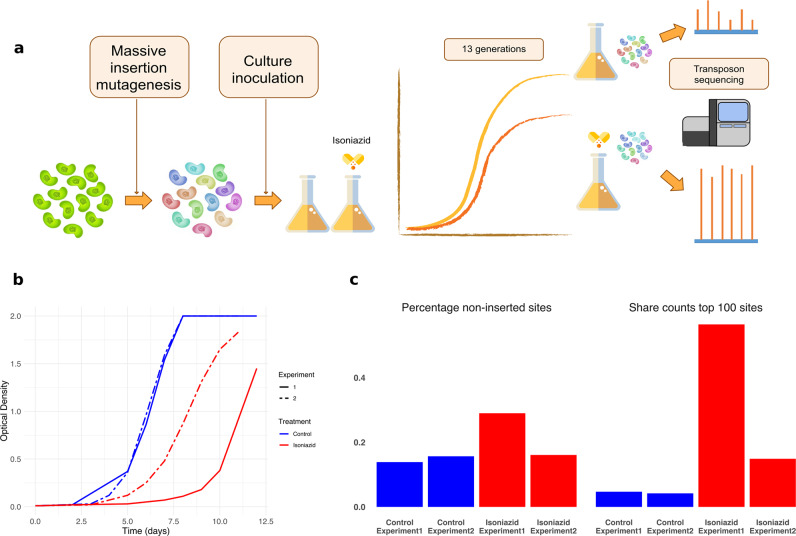
Fig. 1. Transposon sequencing detects changes in response to isoniazid.
a Design of the experiment. Parallel antibiotic-containing and antibiotic-free cultures were inoculated with a saturated insertion mutant pool. After ~13 generations, bacterial DNA was extracted and sequenced to determine the relative abundance of each mutant. b Optical density of the different cultures throughout the experiment. Graph shows that isoniazid partially inhibits bacterial growth. c Isoniazid-containing cultures show strong enrichment of a fraction of insertions indicating a selective advantage relative to the bulk of the population, showing that those cultures experienced higher levels of selection (blue = control, red = isoniazid experiment).