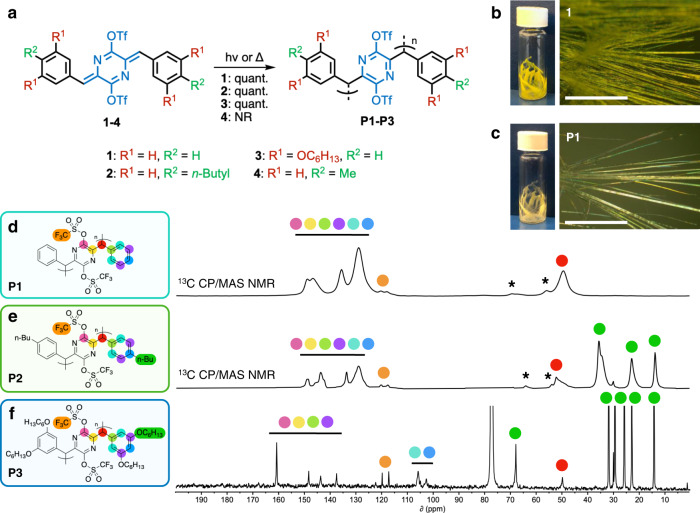
Fig. 1. Single-crystal polymerization of a family of AQM ditriflates.
a The structures of the AQM ditriflates, 1–4, studied herein. Monomers 1–3 underwent topochemical polymerization under the effects of heat and/or light to produce polymers P1–P3. NR: no reaction. b–c Photographs and optical microscope images of vials containing crystals of (b) 1 and (c) P1, showing the typical morphology of crystals. Scale bar: 1 mm. d–f 13C-NMR spectra of polymers P1–P3. Cross-polarization/magic angle spinning (CP/MAS) solid-state 13C-NMR spectra of (d) P1, and (e) P2 (asterisks denote spinning side bands). (f) Solution 13C-NMR spectrum of P3 (solvent: CDCl3). All carbon resonances are annotated by colored circles. The resonances in d–f between 49–53 ppm (red) indicate the presence of the sp3 carbons generated during polymerization, and the CF3 multiplets (expected ratio of 1:3:3:1, but only the two highest peaks are observed) between 117 and 120 ppm (orange) show that the triflate groups remain intact.