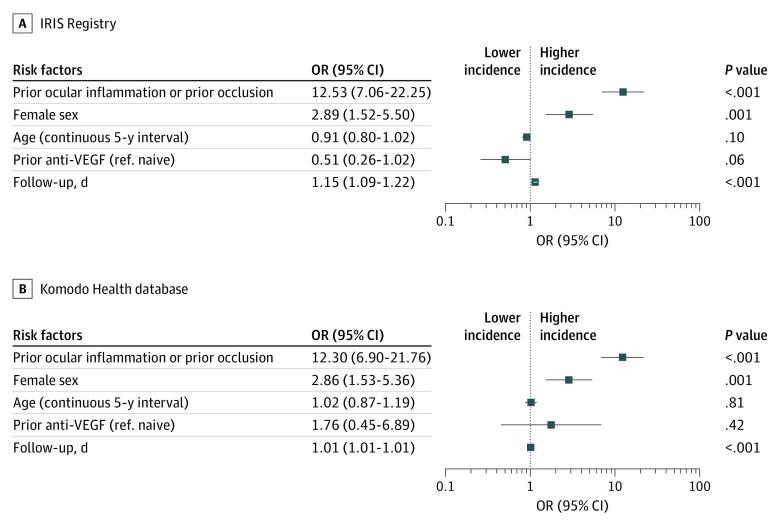
Figure 2. Identification of Potential Risk Factors at Baseline on Estimated Incidence of Retinal Vasculitis and/or Retinal Vascular Occlusion Based on a Multivariable Model.
Retinal vascular occlusion is inclusive of retinal vein occlusion and retinal artery occlusion. The follow-up days variable was used to adjust for varying length of follow-up; graphs are plotted to logarithmic scale, odds ratios (ORs) greater than 1 indicate increased risk of intraocular inflammation and/or retinal vascular occlusion, and ORs less than 1 indicate a decreased risk of intraocular inflammation and/or retinal vascular occlusion. Retinal vascular occlusion represents retinal vasculitis and/or retinal vascular occlusion (59 patient eyes [0.6%] in the Intelligent Research in Sight [IRIS] Registry and 63 patient eyes [0.6%] in the Komodo database). Anti-VEGF indicates anti–vascular endothelial growth factor; ref., reference.