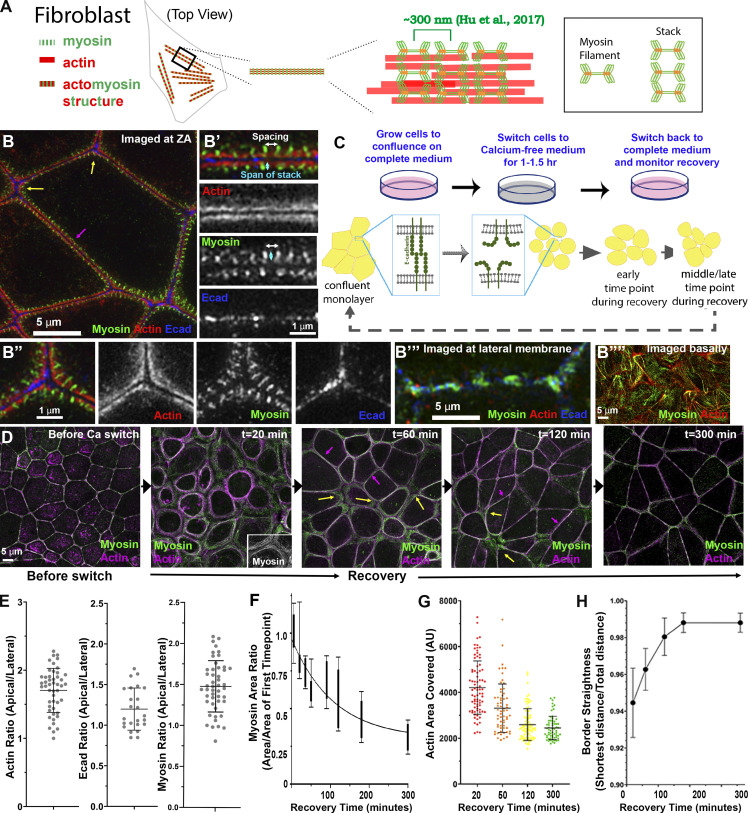
Figure 1.
ZO KD MDCK cells as a model to study formation of ZA actomyosin structures. (A) Schematic of myosin filament stacks in fibroblasts. (B) ZO KD MDCK cells. ZA at bicellular borders (B′) and tricellular junctions (B″). Actin is bundled and myosin organized into a sarcomeric pattern. (B″′) Lateral membrane. (B″″) Basal stress fibers. (C) Schematic diagram of calcium switch. (D) Representative images of actin and myosin at the apical surface as junctions recover. (E) Ratio of apical to lateral signals of actin, Ecad, or myosin at the end of recovery. (F–H) Quantification. Changes of area covered by myosin (F), ZA actin bundling (G), and border curvature (H) during junction maturation. Error bars represent mean ± SD. Magenta arrows, bicellular borders; yellow arrows, tri-/multicellular junctions. Scale bars = 5 µm. For all figures, unless indicated, top-view images are apical MIPs. In E, n = individual borders; actin = 48, Ecad = 24, myosin = 48. In F, numbers for each time point are in Table S1. In H, representative of three experiments with one to three fields of cells/experiment/time point, with seven to nine borders quantified/field.