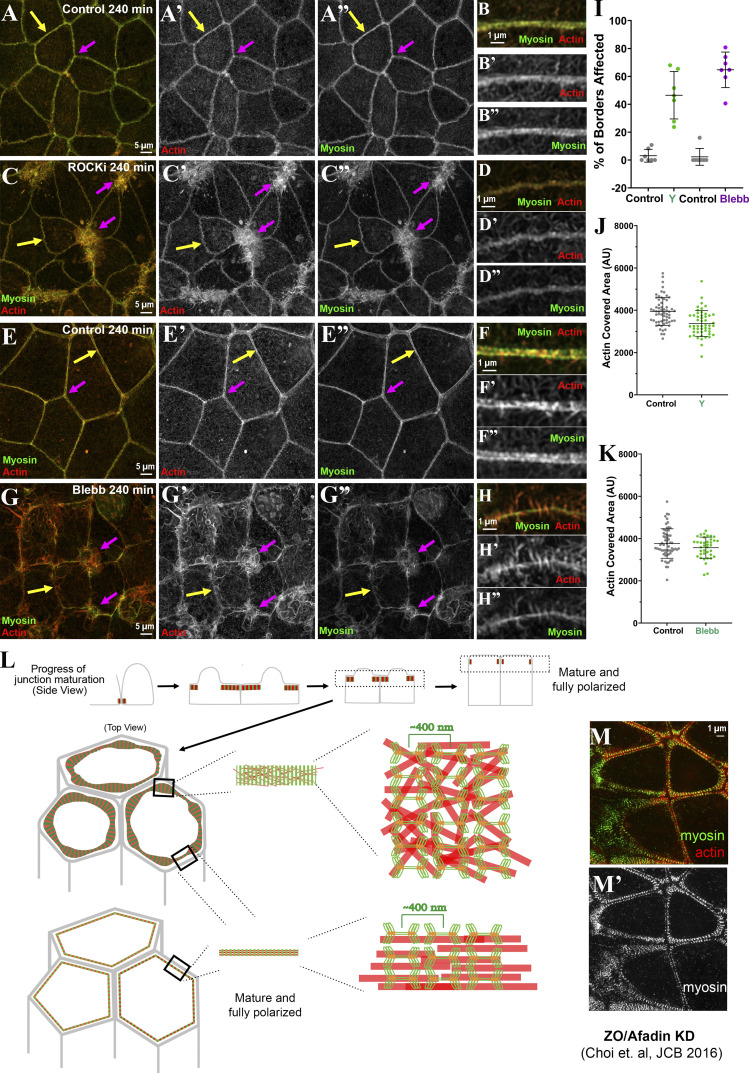
Figure 10.
Inhibiting myosin activation or motor activity disrupts Caco-2 ZA reassembly. (A–D) ROCK inhibition leads to failure to reassemble the ZA at many tricellular and short multicellular junctions (A vs. C, magenta arrows), while bicellular borders are less affected (A vs. C, yellow arrows; B vs. D). (E–H) Blebbistatin disrupts ZA reassembly at most tricellular and short multicellular junctions (E vs. G, magenta arrows), while actin at bicellular borders is more spiky (E vs. G, yellow arrows; F vs. H). (I–K) Quantification, affected bicellular borders (I), and tightening of actin at bicellular borders (J and K). (L) Summary diagram illustrating the model. (M) Broad actin stacks assemble when Afadin is knocked down in ZO-KD MDCK cells. In I, n = 7 fields of cells assessed; in J and K, n = individual borders; control = 62, Y = 50 (J); control = 62, blebb = 38 (K). Error bars represent mean ± SD.