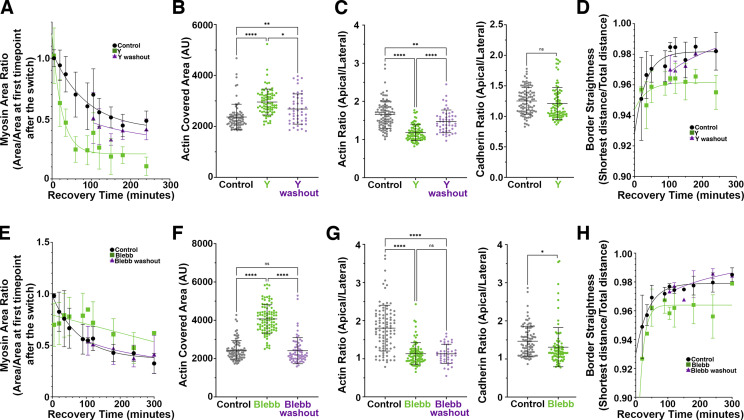
Figure 7.
Myosin activation and motor activity are important for actin bundling and polarization at the ZA. Quantification. (A–D) ROCK inhibition. (E–H) Myosin ATPase inhibition. Inhibiting ROCK reduces junctional myosin (A), while blebbistatin reduces narrowing of myosin stacks (E). Both inhibitors reduce actin bundling at the ZA (B and F), apical actin polarization (C and G, left), and border straightening (D and H). In A and E, numbers for each time point are in Table S1. n = individual borders; control = 80, Y = 80, Y washout = 48 (B); control = 95, Y = 85, Y washout = 49 (C, right); control = 95, Y = 85 (C left); control = 93, blebb = 97, blebb washout = 69 (F); control = 95, blebb = 89, blebb washout =42 (G, right); and control = 95, blebb = 89 (G, left). In D, representative of seven (control, Y) or three (washout) experiments with two fields of cells/experiment/time point, with seven to nine borders quantified/field. In H, representative of five (control, blebb) or two (washout) experiments with two fields of cells/experiment/time point, with seven to nine borders quantified/field. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA tests and post hoc Tukey tests (B, C, F, and G). Error bars represent mean ± SD. ****, P < 0.0001; **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05.