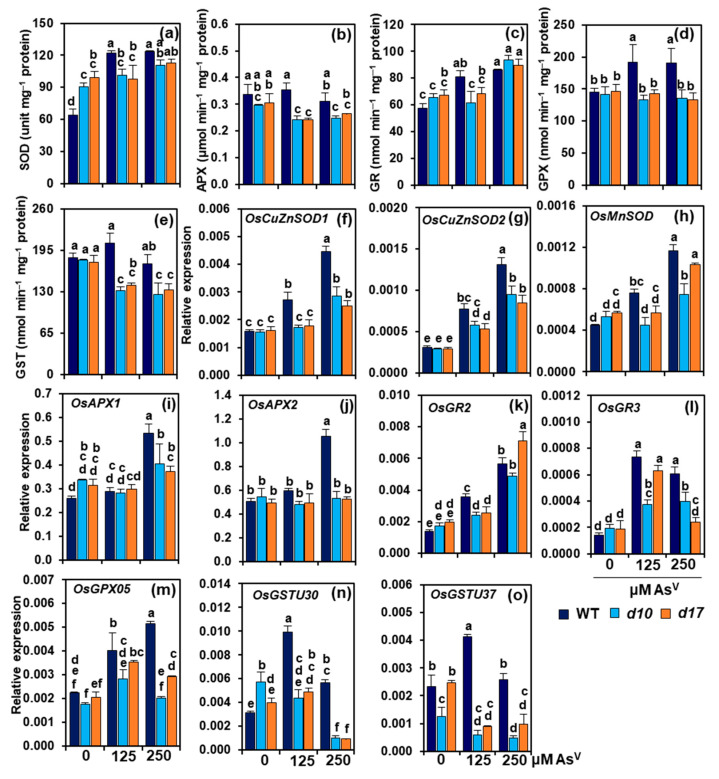
Figure 5.
(a–o) Antioxidant enzyme activities and transcript levels of related genes in the shoots of wild-type (WT) and d10 and d17 mutant plants exposed to different concentrations of sodium arsenate (Na2AsO4; 0, 125 and 250 μM AsV). (a–e) Superoxide dismutase (SOD) (a), ascorbate peroxidase (APX) (b), glutathione reductase (GR) (c), glutathione peroxidase (GPX) (d) and glutathione S-transferase (GST) (e) activities in the shoots of three genotypes on day 3 of AsV treatments. (f–o) Relative expression of biosynthetic genes of SOD (OsCuZnSOD1, OsCuZnSOD2 and OsMnSOD) (f–h), APX (OsAPX1 and OsAPX2) (i,j), GR (OsGR2 and OsGR3) (k,l), GPX (OsGPX05) (m) and GST (OsGSTU30 and OsGSTU37) (n,o) enzymes in the shoots of WT, d10 and d17 on day 3 of the AsV treatments. Represented numerical data are the means with standard errors (n = 3 biological repeats). Significant differences (p < 0.05) among the treatments are denoted by distinct alphabetical letters according to a least significant difference test.