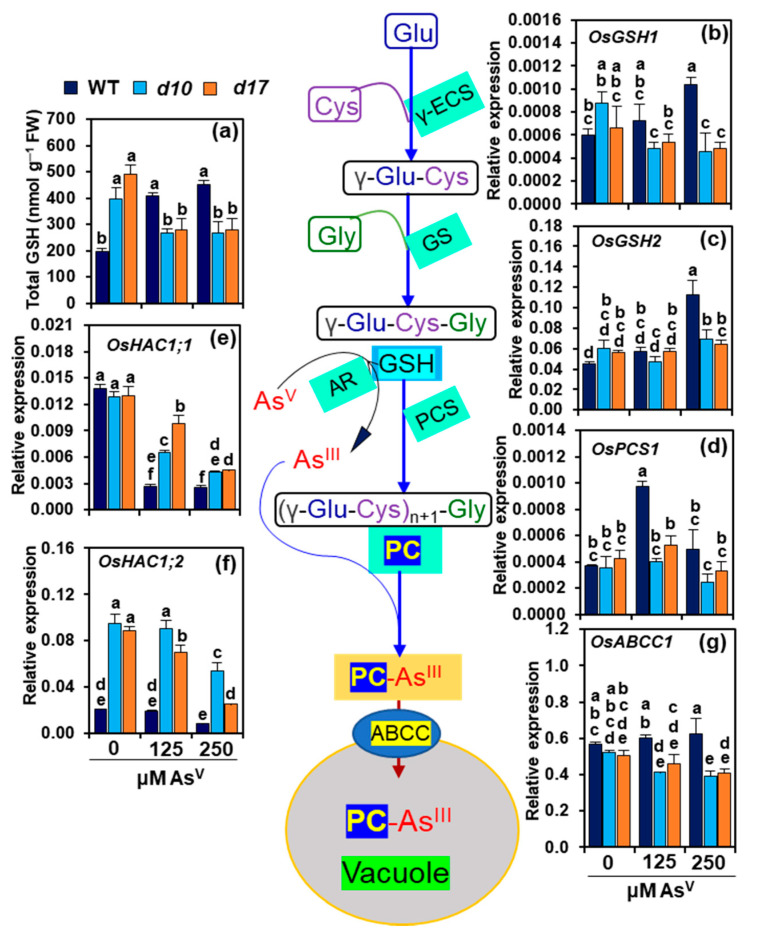
Figure 6.
(a–g) Glutathione (GSH) biosynthesis and GSH-assisted arsenic detoxification in the shoots of wild-type (WT) and d10 and d17 mutant plants exposed to different concentrations of sodium arsenate (Na2AsO4; 0, 125 and 250 μM AsV). Total GSH content (a), and relative expression of genes involved in the biosyntheses of GSH (OsGSH1 (b) and OsGSH2 (c)), phytochelatin synthase, PCS (OsPCS1 (d)), arsenate reductase, AR (OsHAC1;1 (e) and OsHAC1;2 (f)) and C-type ATP-binding cassette, ABCC (OsABCC1 (g)) were determined in the shoots of three genotypes on day 3 of AsV treatments. Represented numerical data are the means with standard errors (n = 3 biological repeats). Significant differences (p < 0.05) among the treatments are denoted by distinct alphabetical letters according to a least significant difference test. AsIII, arsenite; Cys, cysteine; FW, fresh weight; Glu, glutamate; Gly, glycine; γ-ECS, γ-glutamyl cysteine synthetase; GS, glutathione synthetase, HAC, high arsenate content; PC, phytochelatin.