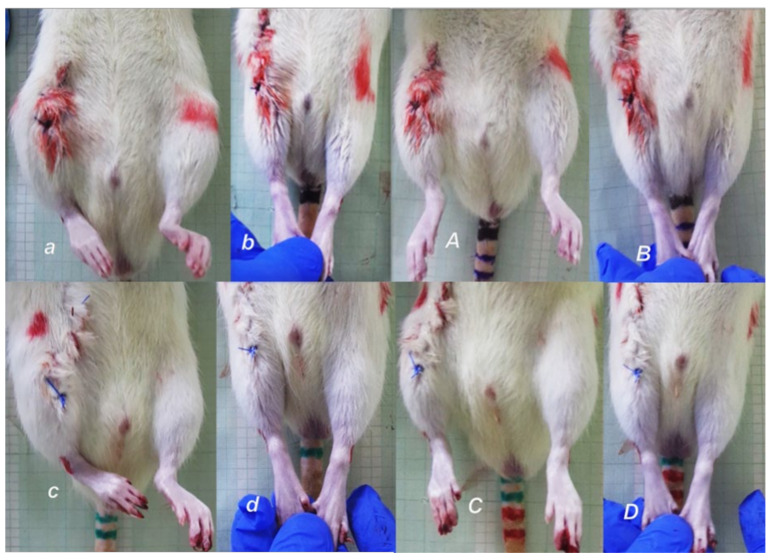
Figure 3.
To assess immediately following post-operative recovery, and to ensure consistency of injury based on this expected deficit in motor function, at 2 h post-injury, close to the end of the anesthesia period, rats, held upright, exhibit the spontaneous injured leg contracture (a,c) that was demonstrated upon leg extension (b,d). Upon BPC 157 10 ng/kg given intragastrically (A,B), leg contracture disappears, in spontaneous presentation (A), or upon maximal legs extension (B). Contrarily, the leg contracture remains unchanged in the controls (water (1 mL/rat) given intragastrically) (C,D).