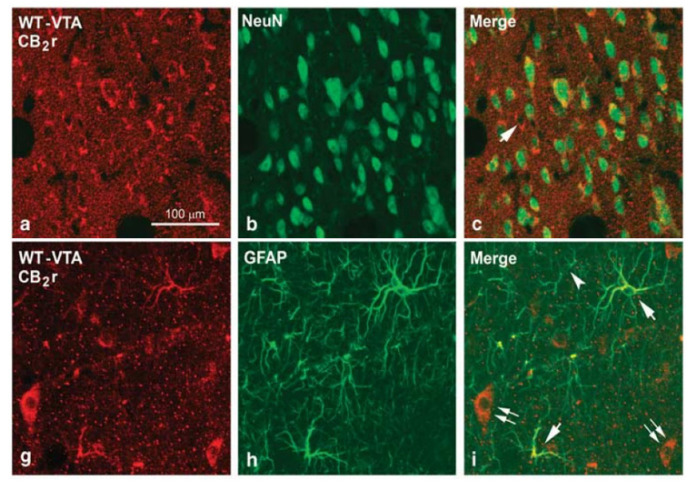
Figure 1.
Confocal photomicrographs showing immunolabeling for CB2 receptors (CB2r), neuronal nuclei (NeuN) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and the nucleus accumbens (NAcc) of wild-type (WT) mice. Double labeling CB2r-NeuN (yellow cells in c) in the VTA and the NAcc and CB2r-GFAP (yellow cells in i) in the VTA indicates the existence of CB2r in neurons and astrocytes. Image adapted from Aracil-Fernandez et al. Neuropsychopharmacology (2012) 37, 1749–1763.