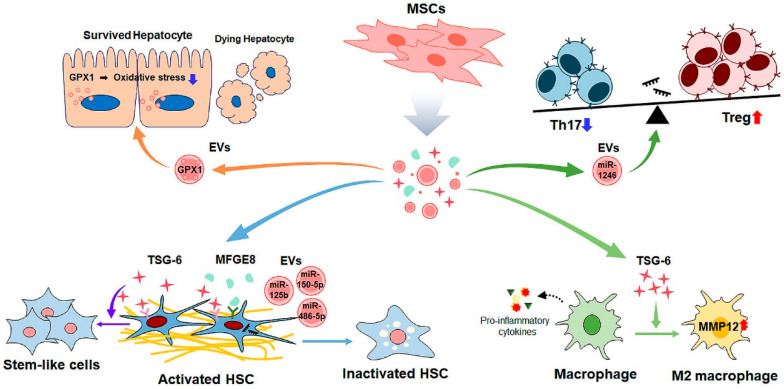
Figure 3.
Therapeutic strategy of MSC-derived secretome and EVs for liver fibrosis. MSCs-derived secretome and extracellular vesicles (EVs) have therapeutic potential for liver fibrosis. In hepatocyte, MSCs-EV delivering glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPX1) reduces oxidative stress, and inhibits hepatocyte death, attenuating liver fibrosis. Several cytokines and EVs targeting HSC also ameliorate liver fibrosis. Tumor necrosis factor-inducible gene 6 protein (TSG-6) induces trans-differentiation of activated HSCs into stem-like cell. Milk Fat Globule EGF Factor 8 protein (MFGE8) and MSCs-EV carrying microRNA (miR) such as miR-486-5p, miR-150-5p and miR-125b reduce liver fibrosis through inactivating HSCs. In addition, MSC-EVs regulate the proportion of T cell by decreasing T helper 17 (Th17) cells and increasing regulatory T (Treg) cells. In macrophage, TSG-6 triggers polarization of M2 macrophage and upregulates MMP12 which suppresses HSC activation.